fwrite in C writes nmemb elements from the given array to the output stream. for each object fputc is called size times (count of bytes for a single element) and file position indicator for the stream is advanced by the number of characters written.
It is declared in stdio.h and takes four arguments. The fwrite function generally used for binary files to write the binary data into the file.
Syntax of fwrite in C:
size_t fwrite(const void * restrict ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb,
FILE * restrict stream);
Where,
ptr: Pointer to the array of elements to be written.
size: Size in bytes of each element to be written.
nmemb: Number of elements to be written.
stream: Pointer to the file, where data will be written.
You might like these articles,
- Pointer in depth.
- Arithmetic operators with a pointer.
- Application of function pointer.
- Function pointer within a structure.
Return value of fwrite():
On success, it returns the number of elements successfully written. On error, it returns a number of elements less than nmemb.
Note: If the size or nmemb is zero, fwrite returns zero and the state of the output stream remains unchanged.
Example code of fwrite in C,
Below example ask the name from the user and store it in the buffer. After getting the name it writes the name in the created file using the fwrite function.
#include <stdio.h>
//Maximum size of the array
#define MAX_SIZE 32
int main()
{
//file pointer
FILE *fp = NULL;
char buffer[MAX_SIZE] = {0};
//Get input from the user
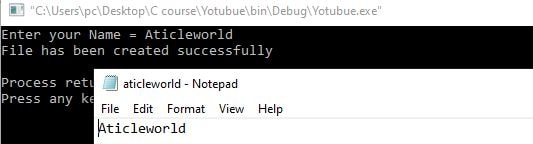
printf("Enter your Name = ");
fgets(buffer,MAX_SIZE,stdin);
//create the file
fp = fopen("aticleworld.txt", "w");
if(fp == NULL)
{
printf("Error in creating the file\n");
exit(1);
}
//Write the buffer in file
fwrite(buffer, sizeof(buffer[0]), MAX_SIZE, fp);
//close the file
fclose(fp);
printf("File has been created successfully\n");
return 0;
}
Output:
Difference between fprintf and fwrite in C:
The difference between fprintf and fwrite is very confusing and most of the people do not know when to use the fprintf and fwrite. Basically, both functions are used to write the data into the given output stream.
fprintf generally use for the text file and fwrite generally use for a binary file. Let see an example code to understand the difference between fprintf and fwrite.
In the below code, I am writing the message length and the message in the file using the fprintf and fwrite function.
Writing the message and the length using the fprintf:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
//file pointer
FILE *fp = NULL;
//Message
char * message = "I love Aticleworld.com";
//Variable for message length
int length = 0;
//create and open the texr file
fp = fopen("aticleworld.txt", "w");
if(fp == NULL)
{
printf("Error in creating the file\n");
exit(1);
}
//Get the length of message
length = strlen(message);
//write the length in file
fprintf(fp,"%d",length);
//write the message in file
fprintf(fp,"%s",message);
//Close the file
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
Output:
In the below image, you can see the fprintf write the 22 (message length) in string format, so it is showing as it as 22.

Writing the message and the length using the fwrite:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
//file pointer
FILE *fp = NULL;
//Message
char * message = "I love Aticleworld.com";
//Variable for message length
int length = 0;
//create and open the binary file
fp = fopen("aticleworld.dat", "wb");
if(fp == NULL)
{
printf("Error in creating the file\n");
exit(1);
}
//Get the length of message
length = strlen(message);
//write the message len in file
fwrite(&length, sizeof(int), 1, fp);
//write message in file
fwrite(message, sizeof(char),length, fp);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
Output:
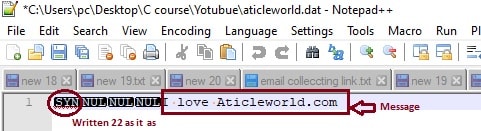
In the below image, you can see the fwrite function write the 22 (Message length) as it as in binary format, so 22 is ASCII value of SYN and it is showing in the file.
I hope now you able to understand the basic difference between fprintf and fwrite. If you have still confusion, then comment in the comment box.
Writing a variable in a file using the fwrite:
Below code writes the value of integer variable data into the file.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//Variable which want to write
int data = 65;
//file pointer
FILE *fp = NULL;
//create and open the text file
fp = fopen("aticleworld.dat", "wb");
if(fp == NULL)
{
printf("Error in creating the file\n");
exit(1);
}
//write the variable in file
fwrite(&data, sizeof(data), 1, fp);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
Writing an array in a file using the fwrite:
Below code writes the entire integer array into the file.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//Variable which want to write
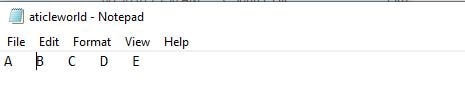
int data[] = {65,66,67,68,69};
//file pointer
FILE *fp = NULL;
//create and open the text file
fp = fopen("aticleworld.dat", "wb");
if(fp == NULL)
{
printf("Error in creating the file\n");
exit(1);
}
//write the array in file
fwrite(data, sizeof(data),1, fp);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
Output:
Writing a structure in a file using the fwrite in C:
you can see this Article, Brief introduction of structure in C
The below code writes the id, first name and last name of the employee using the fwrite into the file.
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct
{
int id;
char fName[16];
char lName[16];
} s_employee;
int main()
{
//Populate structure variable
s_employee sAmlendraInfor = {8886, "Amlendra", "Mishra"};
//file pointer
FILE *fp = NULL;
//create and open the text file
fp = fopen("aticleworld.dat", "wb");
if(fp == NULL)
{
printf("Error in creating the file\n");
exit(1);
}
//write the structure in file
fwrite(&sAmlendraInfor, sizeof(sAmlendraInfor),1, fp);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
Output:

Writing an array of structure in a file using the fwrite in C:
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct
{
int id;
char fName[16];
char lName[16];
} s_employee;
int main()
{
//Populate variable of array of structure
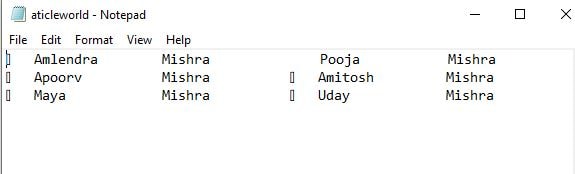
s_employee sAticleworldEmplInfo[] =
{
{1, "Amlendra", "Mishra"},
{2, "Pooja", "Mishra"},
{3, "Apoorv", "Mishra"},
{4, "Amitosh", "Mishra"},
{5, "Maya", "Mishra"},
{6, "Uday", "Mishra"},
};
//file pointer
FILE *fp = NULL;
//create and open the text file
fp = fopen("aticleworld.dat", "wb");
if(fp == NULL)
{
printf("Error in creating the file\n");
exit(1);
}
//write the structure array in file
fwrite(sAticleworldEmplInfo, sizeof(sAticleworldEmplInfo),1, fp);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
Output:
Recommended Articles for you:
- Use of fgetc() function in C?
- How to use fputc() in C?
- You should know fgets() in C?
- fputs() in C?
- Use of fread() in C?
- How to use fopen() in C?
- Use of if condition in C programs.
- Dangling, Void , Null and Wild Pointer.
- How to use fgets() in C?
- C program to convert uppercase to lowercase and vice versa in file
- File handling in C, In a few hours.
- C program to display its own source code as output
- C program to compare two files contents.
- Student Record System Project in C.
- C Program to Create a File & Store Information
- 100 C interview Questions.
