
In C language, we can also create a generic linked list using the void pointer. Generic linked list means that it can store any data type as per the requirements.
The most important thing about the void pointer, it can store the address of any data type. Means that the programmer can store the address of any data type as per there the user requirements.
In the below example, I am creating a Node that contains the void pointer to store the address of any data type and Node pointer to create a link with another node.
Generic Node in C
Using the void pointer, we can create a generic Node. In the below source code I am creating a structure that contains the void pointer and structure pointer.
//Creating a new type
typedef void * pVoid;
// Creating Node
struct Node
{
/*void pointer*/
pVoid iData;
/*Node Pointer*/
struct Node *pNextNode;
};
// Define the new type Node type and Node pointer
typedef struct Node NodeType, * NodePointer;
Function to add a node at the end of the Generic Linked list
It creates an extra node and adds this node in the last of the generic linked list.
/* Paas the reference of the head pointer of a list and
an integer data. This function use to add the node at the End*/
int InsertNodeAtEnd(NodePointer * pHead, void *InputData, int SizeofData)
{
int iRetValue = -1;
int iOffSet = 0;
NodePointer pLastNode = NULL;
NodePointer pNewNode = NULL;
//Give the Address of first Node
pLastNode = *pHead;
// Call malloc to allocate memory in heap for the new node
pNewNode = malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
if( pNewNode != NULL) //Check allocated memory
{
pNewNode->iData = malloc(SizeofData); //put the desire Data
//Copy the bytes of data as per the data types
for (iOffSet = 0; iOffSet < SizeofData; iOffSet++)
*((uint8_t *)(pNewNode->iData + iOffSet)) = *((uint8_t *)(InputData + iOffSet));
pNewNode->pNextNode = NULL; //Give the Address of first Node
iRetValue = 0; // Update the return value
}
// If there is no node in beginning
if(pLastNode == NULL)
{
*pHead = pNewNode;
}
else
{
// Find the address of last node
while( pLastNode ->pNextNode != NULL)
{
pLastNode = pLastNode ->pNextNode;
}
// Assign last node address
pLastNode ->pNextNode = pNewNode;
}
return iRetValue;
}
Free the all allocated memory
We know that when we allocate memory in heap then this memory alive till the life of the program. So after use of this memory, we have to free all the allocated memory either we will get memory leak issues.
/* Paas the reference of the head pointer of a list. This function use
to free the all allocated memory*/
void FreeAllocatedMemory(NodePointer *pHead)
{
NodePointer pTmpNode = NULL;
NodePointer pFirstNode = NULL;
//Assign the Address of first node
pFirstNode = *pHead;
/*check if pFirstNode is NULL, then now list is empty,
so assign NULL to head and return.*/
while (pFirstNode != NULL)
{
/*Save the pFirstNode in a pTmpNode node pointer*/
pTmpNode = pFirstNode ;
/*Assign the address of next on your list*/
pFirstNode = pFirstNode->pNextNode;
//Free the data
free(pTmpNode->iData);
//Free the allocated memory
free(pTmpNode );
}
//Assign NULL to the head pointer
*pHead = NULL;
}
If you want to learn more about the c language, here 10 Free days (up to 200 minutes) C video course for you.
Your free trial is waiting
Driver program to create a generic linked list
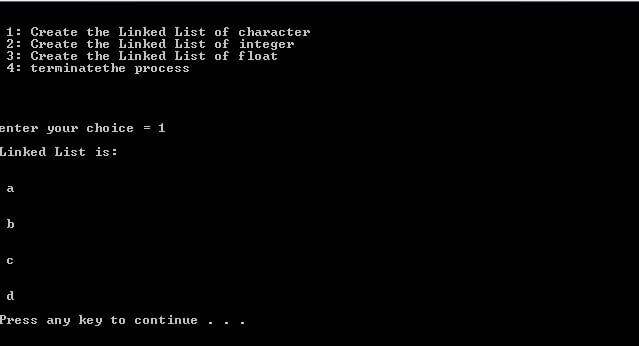
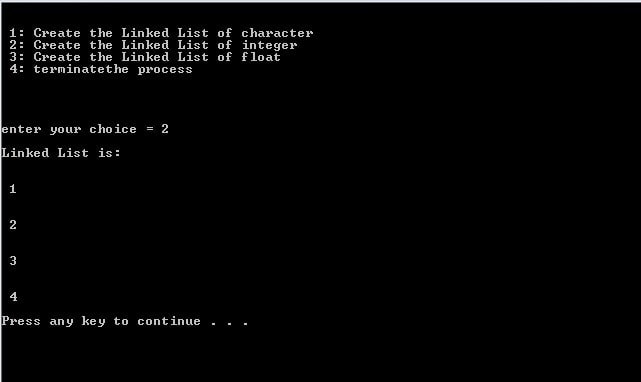
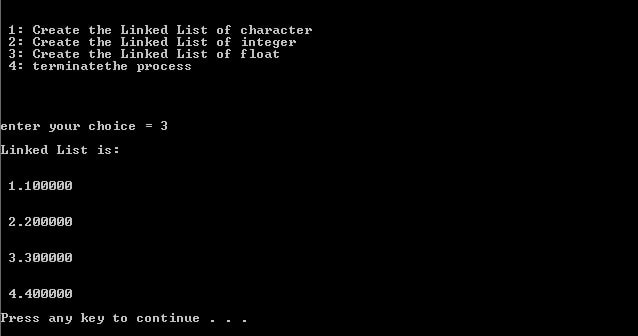
In the below program user can create a linked-list as per their requirements. If the user selects 1 then the program creates a list of a character and if select 2 then create a list of an integer and if the user select 3 then create a list of the float.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
//Calculate size of buffer element
#define DATA_SIZE(y) sizeof(y[0])
//Calculate number of element in buffer
#define Number_Node(x) sizeof(x)/DATA_SIZE(x)
//Creating a new type
typedef void * pVoid;
// Creating Node
struct Node
{
/*void pointer*/
pVoid iData;
/*Node Pointer*/
struct Node *pNextNode;
};
//Define the new type Node type and Node pointer
typedef struct Node NodeType, * NodePointer;
//Print character
void PrintTheCharater(NodePointer pNode)
{
//Clear the screen
printf("\nLinked List is: \n\n");
while (pNode != NULL)
{
printf("\n %c\n\n",*((char *)pNode->iData));
pNode = pNode->pNextNode;
}
system("pause");
}
//Print integer
void PrintTheInteger(NodePointer pNode)
{
//Clear the screen
printf("\nLinked List is: \n\n");
while (pNode != NULL)
{
printf("\n %d\n\n",*((int *)pNode->iData));
pNode = pNode->pNextNode;
}
system("pause");
}
//Print float
void PrintTheFloat(NodePointer pNode)
{
//Clear the screen
printf("\nLinked List is: \n\n");
while (pNode != NULL)
{
printf("\n %f\n\n",*((float *)pNode->iData));
pNode = pNode->pNextNode;
}
system("pause");
}
/* Paas the reference of the head pointer of a list and
an integer data. This function use to add the node at the End*/
int InsertNodeAtEnd(NodePointer * pHead, void *InputData, int SizeofData)
{
int iRetValue = -1;
int iOffSet = 0;
NodePointer pLastNode = NULL;
NodePointer pNewNode = NULL;
//Give the Address of first Node
pLastNode = *pHead;
// Call malloc to allocate memory in heap for the new node
pNewNode = malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
if( pNewNode != NULL) //Check allocated memory
{
pNewNode->iData = malloc(SizeofData); //put the desire Data
//Copy the bytes of data as per the data types
for (iOffSet = 0; iOffSet < SizeofData; iOffSet++)
{
*((uint8_t *)(pNewNode->iData + iOffSet)) = *((uint8_t *)(InputData + iOffSet));
}
pNewNode->pNextNode = NULL; //Give the Address of first Node
iRetValue = 0; // Update the return value
}
// If there is no node in beginning
if(pLastNode == NULL)
{
*pHead = pNewNode;
}
else
{
// Find the address of last node
while( pLastNode ->pNextNode != NULL)
{
pLastNode = pLastNode ->pNextNode;
}
// Assign last node address
pLastNode ->pNextNode = pNewNode;
}
return iRetValue;
}
/* Paas the reference of the head pointer of a list. This function use
to free the all allocated memory*/
void FreeAllocatedMemory(NodePointer *pHead)
{
NodePointer pTmpNode = NULL;
NodePointer pFirstNode = NULL;
//Assign the Address of first node
pFirstNode = *pHead;
/*check if pFirstNode is NULL, then now list is empty,
so assign NULL to head and return.*/
while (pFirstNode != NULL)
{
/*Save the pFirstNode in a pTmpNode node pointer*/
pTmpNode = pFirstNode ;
/*Assign the address of next on your list*/
pFirstNode = pFirstNode->pNextNode;
//Free the data
free(pTmpNode->iData);
//Free the allocated memory
free(pTmpNode );
}
//Assign NULL to the head pointer
*pHead = NULL;
}
//Create a linked list of certain number of nodes
int CreateLinkedList(NodePointer *pHead, void *InputData, int SizeofData)
{
int iRetValue = -1;
int iOffSet = 0;
NodePointer pNewNode = NULL;
if((*pHead) == NULL)
{
// Call malloc to allocate memory in heap for the first node
pNewNode = malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
if( pNewNode != NULL) //Check allocated memory
{
pNewNode->iData = malloc(SizeofData); //put the desire Data
//Copy the bytes of data as per the data types
for (iOffSet = 0; iOffSet < SizeofData; iOffSet++)
{
*((uint8_t *)(pNewNode->iData + iOffSet)) = *((uint8_t *)(InputData + iOffSet));
}
pNewNode->pNextNode = NULL; //Give the Address of first Node
*pHead = pNewNode; /*Assign the address of
the first node to the head pointer*/
iRetValue = 0; // Update the return value
}
}
else
{
//Add the Node at the End
iRetValue = InsertNodeAtEnd(pHead,InputData,SizeofData);
}
return iRetValue;
}
int main(void)
{
int iRetValue = -1;
int iChoice = 0;
int iNumberNode =0;
int iCount = 0;
int iPosition =0;
/*Start with the empty list */
NodePointer head = NULL;
while(1)
{
//Clear the screen
system("cls");
//Select the Choice as per the requirements
printf("\n\n\
1: Create the Linked List of character\n\
2: Create the Linked List of integer\n\
3: Create the Linked List of float\n\
4: terminatethe process \n\n\n");
printf("\n\nenter your choice = ");
scanf("%d",&iChoice);
switch(iChoice)
{
case 1:
{
char acBuffer[4] = {'a','b','c','d'};
iNumberNode = Number_Node(acBuffer);
for(iCount =0; iCount <iNumberNode ; iCount++)
{
CreateLinkedList(&head, (acBuffer + iCount),DATA_SIZE(acBuffer));
}
PrintTheCharater(head);
break;
}
case 2:
{
int acBuffer[4] = {1, 2, 3, 4};
iNumberNode = Number_Node(acBuffer);
for(iCount =0; iCount <iNumberNode ; iCount++)
{
CreateLinkedList(&head, (acBuffer + iCount),DATA_SIZE(acBuffer));
}
PrintTheInteger(head);
break;
}
case 3:
{
float acBuffer[4] = {1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4};
iNumberNode = Number_Node(acBuffer);
for(iCount =0; iCount <iNumberNode ; iCount++)
{
CreateLinkedList(&head, (acBuffer + iCount),DATA_SIZE(acBuffer));
}
PrintTheFloat(head);
break;
}
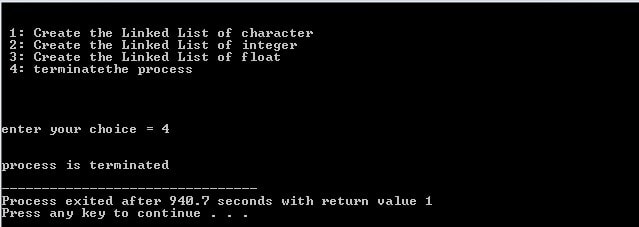
case 4:
{
printf("\n\nprocess is terminated\n ");
exit(1);
}
default:
{
printf("Invalid choice\n");
system("pause");
break;
}
}
//Free all allocated memory
FreeAllocatedMemory(&head);
}
return 0;
}
OutPut:
When user Enter: 1
When user Enter: 2
When user Enter: 3
When user Enter: 4



Arithmetic on void* is not allowed in C/C++, but there is however one extension in GCC that allows it.
The above examples can be compiled only on GCC. In order to keep generality, I would use:
“*(((uint8_t *)pNewNode->iData + iOffSet)) = *(((uint8_t *)InputData + iOffSet));”
instead of
“*((uint8_t *)(pNewNode->iData + iOffSet)) = *((uint8_t *)(InputData + iOffSet));”.