In my previous article, we have seen the introduction of the batch file (batch script). In this article, I will describe some important commands of the batch file which frequently used. Below find the list of the commands.
Note: Batch file commands are not case sensitive.
ASSOC
Displays or modifies file name extension associations. If used without parameters, assoc displays a list of all the current file name extension associations.
Note: This command is only supported within CMD.EXE and is not available from PowerShell.
Example,
@echo OFF assoc .txt
Output:
.txt = textfile
ATTRIB
ATTRIB command is used to displays, sets or removes attributes assigned to files or directories. If we used this command without parameters, display attributes of all files in the current directory.
Example,
To display the attributes of a file named test that is located in the current directory, type:
@echo OFF ATTRIB test.txt
To assign the Read-only attribute to the file named test.txt, type:
ATTRIB +r test.txt
To remove the Read-only attribute from files in the Public directory and its subdirectories on a disk in drive B, type:
@echo OFF ATTRIB -r b:\public\*.* /s
AT
Schedules commands and programs to run on a computer at a specified time and date. You can use at only when the Schedule service is running. Used without parameters, at lists scheduled commands.
ARP
The ARP command is used to displays and modifies entries in the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache. The ARP cache contains one or more tables that are used to store IP addresses and their resolved Ethernet or Token Ring physical addresses.
There is a separate table for each Ethernet or Token Ring network adapter installed on your computer. Used without parameters, arp displays help information.
Example,
To display the arp cache tables for all interfaces, type:
arp /a
To display the arp cache table for the interface that is assigned the IP address 10.0.0.99, type:
arp /a /n 10.0.0.99
To add a static arp cache entry that resolves the IP address 10.0.0.80 to the physical address 00-AA-00-4F-2A-9C, type:
arp /s 10.0.0.80 00-AA-00-4F-2A-9C
CD
The batch command CD helps in navigating through different directories and changing directories or displaying current directory.
Example,
@echo off Rem The cd without any parameters is used to displaying the current working directory cd Rem Changing the path to Program Files cd\Program Files cd Rem Changing the path to Program Files cd %USERPROFILE% cd Rem Changing to the parent directory cd.. cd Rem Changing to the parent directory two levels up cd..\.. cd
Output:
C:\Users\Administrator C:\Program Files C:\Users\Administrator C:\Users C:\
CHKDSK
The batch command CHKDSK is used for checking errors in the disk.
Example,
@echo OFF CHKDSK
CHOICE
In the batch script, choice command prompts the list of single-character choices and allows the user to select one item from the list.
Syntax,
choice [/c [<Choice1><Choice2><…>]] [/n] [/cs] [/t <Timeout> /d <Choice>] [/m <“Text”>]
Parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
| /c <Choice1><…> | Specifies the list of choices to be created. Valid choices include a-z, A-Z, 0-9, and extended ASCII characters (128-254). The default list is “YN”, which is displayed as [Y,N]?. |
| /n | Hides the list of choices, although the choices are still enabled and the message text (if specified by /m) is still displayed. |
| /cs | Specifies that the choices are case-sensitive. By default, the choices are not case-sensitive. |
| /t <Timeout> | Specifies the number of seconds to pause before using the default choice specified by /d. Acceptable values are from 0 to 9999. If /t is set to 0, choice does not pause before returning the default choice. |
| /d <Choice> | Specifies the default choice to use after waiting the number of seconds specified by /t. The default choice must be in the list of choices specified by /c. |
| /m <“Text”> | Specifies a message to display before the list of choices. If /m is not specified, only the choice prompt is displayed. |
| /? | Displays help at the command prompt. |
Note: The ERRORLEVEL environment variable is set to the index of the key that the user selects from the list of choices. The first choice in the list returns a value of 1, the second a value of 2, and so on. If the user presses a key that is not a valid choice, choice sounds a warning beep. If choice detects an error condition, it returns an ERRORLEVEL value of 255. If the user presses CTRL+BREAK or CTRL+C, choice returns an ERRORLEVEL value of 0.
Example script,
In the below script I have created a list of A, B and C. here choice command will invoke the list and ask the user to select the character from the list.
@ECHO OFF :BEGIN CLS CHOICE /N /C:ABC /M "Select Character(A, B, or C)" IF ERRORLEVEL ==3 GOTO THREE IF ERRORLEVEL ==2 GOTO TWO IF ERRORLEVEL ==1 GOTO ONE GOTO END :THREE ECHO YOU HAVE PRESSED C GOTO END :TWO ECHO YOU HAVE PRESSED B GOTO END :ONE ECHO YOU HAVE PRESSED A :END pause
CLS
This command is used to clear the console screen.
Example,
@echo OFF CLS pause
CMD
This batch command invokes a new command prompt window.
Example,
@echo OFF CMD
COMP
The COMP batch command compares the size of two files and checks if they are different in size.
Example,
@echo OFF COMP C:\data1.txt C:\data2.txt
CONVERT
The CONVERT batch commands the volumes or drives from one format to another i.e from FAT to NTFS.
Example,
@echo OFF CONVERT D:\
COPY
The COPY command is used for copying files from one location to another location.
Syntax,
Copy [source] [destination]
Example,
In below, I am copying a file (Test.txt) from one drive (D) to another drive (E).
COPY D:\Test.txt E:\
DATE
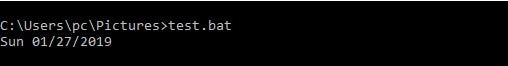
The DATE command displays the current date of the system.
Example,
@echo OFF echo %DATE%
DISKPART
The batch command DISKPART shows the properties of a disk partition.
Example,
@echo OFF DISKPART
DRIVERQUERY
This batch command displays all the drivers installed and their properties.
Example,
@echo OFF DRIVERQUERY
DEL
DEL command is used to delete files.
Syntax,
del [filename]
Example,
- To delete a single file Test.txt.
DEL D:\Test.txt
- Delete all the files of .txt extensions and ask for confirmation before deleting.
DEL /p/s D:\*.txt
- Delete all the files of .txt extensions and not ask for confirmation before deleting.
DEL /s D:\*.txt
DIR
DIR command lists all the contents of directories.
- List all the contents of the current directory.
DIR
- Lists all files with .txt extension.
DIR *.txt
- Lists all hidden files only.
DIR /ah
- List files with hidden files.
DIR /a
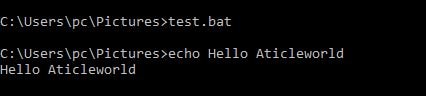
ECHO
ECHO command is used to display the message on the console or turns echoing commands on/off.
Example,
echo Hello Aticleworld
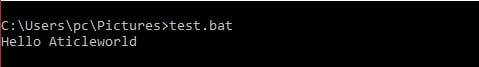
You can see that in the below example command itself displaying on the console. So using the echo you can also off the displaying the commands on the console.
See example,
@echo OFF echo Hello Aticleworld
EXPAND
The EXPAND batch command extracts the contents of the compressed .cab cabinet files file.
Example,
@echo OFF EXPAND test.cab
This script will extract all the contents of the test.cab file to the same location where test.cab is located.
EXIT
EXIT command terminates and exits the console.
Example,
@echo off echo "Hello Aticleworld" exit
FC
The FC batch command finds the difference between the two files and displays them to console.
Example,
@echo OFF FC D:\test1.txt D:\test2.txt
FIND
Find (batch file commands) is used to search the specified string in a file or files and displays lines of text that contain the specified string.
Syntax:
find [/v] [/c] [/n] [/i] [/off[line]] “string” [[Drive:][Path]FileName]
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
| /v | Displays all lines that do not contain the specified <String>. |
| /c | Counts the lines that contain the specified <String>and displays the total. |
| /n | Precedes each line with the file’s line number. |
| /i | Specifies that the search is not case-sensitive. |
| [/off[line]] | Does not skip files that have the offline attribute set. |
| “<String>” | Required. Specifies the group of characters (enclosed in quotation marks) that you want to search for. |
| [<Drive>:][] | Specifies the location and name of the file in which to search for the specified string. |
| /? | Displays help at the command prompt. |
Example,
The below script will search for the string “aticleworld” in my.txt file. If the specified string exists in my.txt, it will display the corresponding line.
@echo OFF FIND "aticleworld" my.txt
FORMAT
The FORMAT batch command is used to format Windows-supported file systems such as FAT 16/32 or NTFS.
Example,
The below script will format the E drive.
@echo OFF FORMAT E:\
HELP
This batch command shows the list of Windows-supplied commands.
IPCONFIG
The batch command IPCONFIG displays Windows IP configuration.
Example,
@echo OFF IPCONFIG
LABEL
The LABEL batch command displays the label of a drive or volume and is also is used for adding, setting or removing a disklabel.
Example,
@echo OFF LABEL
MD
This batch command creates a new directory or folder in the working directory.
Example,
The below script will create a new directory test in the current working location.
@echo OFF MD test
MORE
This batch command displays the content of a file one by one.
Example,
@echo OFF MORE D:\test.txt
Note: In order to proceed and display the remaining contents of the file, you need to enter a key.
NET
The batch command NET is used for many network functionalities depending upon the commands used.
Syntax,
NET [variant]
Where its variants can be one of the following,
- net accounts.
- net computer.
- net config.
- net continue.
- net file.
- net group.
- net help.
- net helpmsg.
- net localgroup.
- net name.
- net pause.
- net print.
- net send.
- net session.
- net share.
- net start.
- net statistics.
- net stop.
- net time.
- net use.
- net user.
- net view.
PING
This batch command is used for sending ICMP/IP packets to the designated address over the network.
Example,
Below script will send packets to address 127.0.1.1
@echo OFF PING 127.0.1.1
Output:
Pinging 127.0.1.1 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 127.0.1.1: bytes = 32 time<1ms TTL = 128 Reply from 127.0.1.1: bytes = 32 time<1ms TTL = 128 Ping statistics for 127.0.1.1: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
MOVE
MOVE command moves files or directories between directories or renames the directories.
Syntax,
MOVE [source] [destination]
Example,
- move Test.txt from dir1 to dir2.
MOVE D:\dir1\Test.txt D:\dir2
- Rename directory dir1 to dir2.
MOVE E:\dir1 E:\dir2
- Rename fileTest.txt to Test1.txt.
MOVE E:\Test.txt E:\Test1.txt
- Move directory dir1 from E:\ to E:\Test.
MOVE E:\dir1 E:\Test\
PAUSE
PAUSE command is used for holding the console screen till the user enters input value.
@echo OFF ECHO Hello Aticleworld pause
REM
This command is used to put a comment in the batch script.
Example,
@echo OFF REM This is a comment
REN
The batch command REN is used for renaming files and directories.
Example,
@echo OFF REM To rename x.php to y.php REN C:\Test1.C C:\Test2.c
SET
Displays, sets, or removes CMD.EXE environment variables. If used without parameters, set displays the current environment variable settings.
Example,
@echo OFF SET
SHUTDOWN
The SHUTDOWN command enables you to shut down or restart local or remote computers one at a time.
Example,
@echo OFF SHUTDOWN
SORT
The batch command SORT reads input, sorts data, and writes the results to the screen, to a file, or to another device.
START
The batch command START is used to open a file or start a new program.
Example,
The below script will start the application paint if it is in the working location, else you will have to explicitly indicate the path of that program as well.
@echo OFF START paint.exe
SYSTEMINFO
The batch command SYSTEMINFO displays detailed configuration information about a computer and its operating system, including operating system configuration, security information, product ID, and hardware properties (such as RAM, disk space, and network cards).
Example,
@echo OFF SYSTEMINFO
TASKLIST
The TASKLIST command displays a list of currently running processes on the local computer or on a remote computer. Tasklist replaces the tlist tool.
Example,
@echo OFF TASKLIST
TIME
The batch command TIME is used to display or set the system time. If used without parameters, time displays the current system time and prompts you to enter a new time.
Example,
@echo OFF ECHO %TIME%
Output:
8:47:05.00
TIMEOUT
The TIMEOUT command is used to pauses the command processor for the specified number of seconds.
Example,
To pause the command processor for ten seconds, type:
timeout /t 10
TITLE
The batch command TITLE sets the new title for output console.
Example,
@echo OFF TITLE Aticleworld
TREE
The tree command displays the directory structure of a path or of the disk in a drive graphically.
TYPE
The batch command TYPE is used for displaying the content of a file to an output console.
Example,
The below script will display all the contents of test.txt to the console.
@echo OFF TYPE C:\test.txt pause
VER
The batch command VER displays the operating system version number.
Note: This command is supported in the Windows Command prompt (Cmd.exe), but not in PowerShell.
Example,
@echo OFF VER pause
VOL
The batch command VOL displays the current volume label of Windows.
Example,
@echo OFF VOL
where
The where batch command displays the location of files that match the given search pattern.
Examples,
To find all files named “Test” in drive C of the current computer and its subdirectories, type. here /r is for subdirectory search.
where /r c:\ test
XCOPY
The batch command XCOPY is similar to COPY command but COPY command copies single file whereas XCOPY command copies entire directories including subdirectories.
Example,
The below script will copy test.txt from D drive to E drive.
@echo OFF XCOPY D:\test.txt to E:\
If you want to add another batch file commands in this list, then your welcome. I will publish the mentioned batch file commands with your name. If you have any other suggestions for this batch file commands list, then please write in the comment box either you can directly email to admin@aticleworld.com.
In the Last, I will also try to create a free eBook of batch script commands (batch file commands PDF) with its usage.
Recommended Articles for you:
- Batch file introduction.
- How to create variables in the batch script.
- Batch script to copy files from one folder to another folder.
- How to use if-else statements in the batch script.
- for loop in the batch file.
- List of Linux Commands.
