In this tutorial, you will learn the difference between char array and char pointer (char [] vs char *). Both array and pointer have a close relationship to each other but both are different types and have different concepts in C programming. You can consider other important topics:
- Difference between pointer and array in C.
- Difference between pointer to an array and array of pointers.
- What is a memory leak and how we can avoid it?
- 15 mistakes with memory allocation in C.
Let’s consider the following example to understand the difference between the character array and character pointer in C.
void test()
{
//arr is array of characters
char arr[12] = "Aticleworld";
//ptr is pointer to char
char *ptr = "Aticleworld";
}
Following the difference between char array and char pointer in C:
Now, let’s compare arr ( array of characters) and ptr (character pointer).
1. A character string literal is a sequence of zero or more multibyte characters enclosed in double-quotes. When you are writing the statement char arr[12] = "Aticleworld", the characters from the string literal are copied into arr.
On the other hand, when you are writing the statement char *ptr = "Aticleworld", you are letting the string literal array undergo array-to-pointer conversion to get a pointer to its first element. The pointer ptr is pointing at the first element of the string literal array ('A').
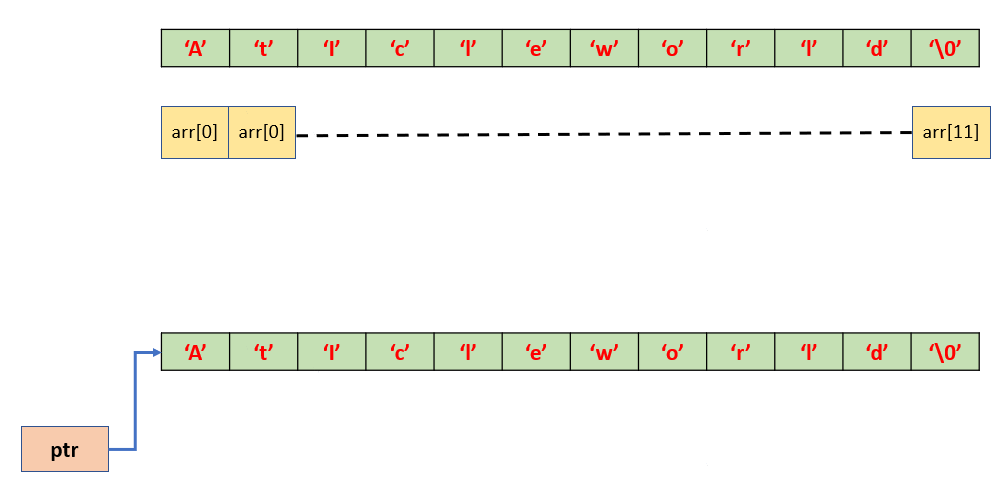
2. arr is a collection of characters stored at a contiguous memory location whereas ptr holds the address of the character.
See the above image, arr which contains 12 elements and each element is on a contiguous memory location. On the other hand, ptr hold the address of the first character of strings literal.
3. When we use the sizeof operator on the char array arr it gives the total number of characters whereas char pointer ptr only gives the size of the pointer. Example,
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//arr is array of characters
char arr[] = "Aticleworld";
//ptr is pointer to char
char *ptr = "Aticleworld";
printf("Size of arr %ld\n", sizeof(arr));
// sizeof a pointer is printed which is same for all type
// of pointers (char *, void *, etc)
printf("Size of ptr %ld", sizeof(ptr));
return 0;
}
Output:
Size of arr 24 Size of ptr 4
4. Another important difference between array and pointer is that we can increment the pointer but we can not create the increment the array. Example,
arr++ => illegal statment. ptr++ ==> legal statement.
5. We can reassign the value to the array but string literals are not modifiable. If a program attempts to modify the static array formed by a string literal, the behavior is undefined. Example,
//arr is array of characters
char arr[] = "Aticleworld";
gets(arr);
fgets(arr,sizeof(arr),stdin); //valid expression
scanf("%s", arr); //valid expression
strcpy(arr, "aticle"); //valid expression
arr[0] = 'a'; //valid expression
arr[10] = 'M'; //valid expression
arr[11] = 'M'; //valid expression
char *ptr = "Aticleworld"; ptr[0] = 'P'; //Invalid expression *ptr = 'W'; //Invalid expression
6. An uninitialized pointer may also lead to undefined behavior. See the below example.
char *ptr;
ptr[0] = 'A'; //Undefined Behavior
gets(ptr); //Undefined Behavior
scanf("%s", ptr); //Undefined Behavior
strcpy(ptr, "source"); //Undefined Behavior
strcat(ptr, "second string"); //Undefined Behavior
7. Char array static in nature means you could not resize the size of the array whereas with a pointer you can change the size of allocated memory at any point in time.
8.A char array is fully controlled by the scope. It will allocate the needed memory correctly and automatically release the memory when goes out of the scope. But the situation with the char pointer is different if you allocate the dynamic memory, you have to deallocate it manually otherwise it introduce memory leaks. Example,
//ok
void foo1()
{
//arr is array of characters
char arr[12] = "Aticleworld";
}
//Issue memory leak
void foo2()
{
char *ptr = (char*)malloc(12);
//forget to free the memory..
}
Recommended Articles for you:
- C Programming Courses And Tutorials.
- new operator in C++ for dynamic memory
- malloc vs calloc.
- How to pass an array as a parameter in C?
- How to create dynamic array in C?
- 15 Common mistakes with memory allocation.
- Interview Questions on Arrays.
- How to access a two-dimensional array using pointers in C?
- Arithmetic operation on pointer in C.
- A brief description of the pointer in C.
- Dangling, Void, Null and Wild Pointers
- Function pointer in c, a detailed guide