The strstr function returns a pointer to the first occurrence of string s2 in string s1. The function returns the null pointer if the string is not found. The process of matching does not include the terminating null-characters(‘\0’).
Syntax of strstr in C:
char *strstr(const char *s1, const char *s2);
Parameters:
s1 − This is the pointer to a string to be scanned.
s2 − This is the pointer to a string containing the sequence of characters to match.
Return:
The strstr function returns a pointer to the located string, or a null pointer if the string is not found. If s2 points to a string with zero length, the function returns s1.
Let’s see an example code to understand the usage of the strstr in C.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
//Define a pointer of type char, a string and the substring to be found
char *ptr;
char s1[] = "Aticleworld.com";
char s2[] = ".com";
//Find memory address where s2 ",com" is found in s1
ptr = strstr(s1, s2);
//Print out the character at this memory address, i.e. '.'
printf("%c\n", *ptr);
//Print out return string"
printf("%s\n", ptr);
return 0;
}
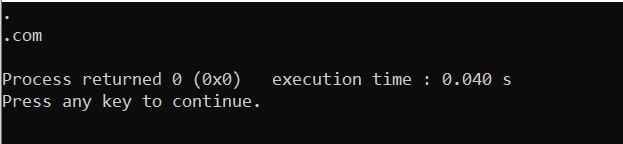
Output:
ptr is now a pointer to the 12th letter (.) in “Aticleworld.com”.
Some important points related to strstr function:
1.) We must include string.h header file before using the strstr function in C.
2.) The strstr function returns a null pointer if the string is not found. Let’s see an example code,
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
//Define a pointer of type char, a string and the substring to be found
char *ptr;
char s1[] = "Aticleworld.com";
char s2[] = "ABC";
//Find memory address where s2 "ABC" is found in s1
ptr = strstr(s1, s2);
if(ptr == NULL)
{
//Sub string not found
printf("Sub string not found");
}
else
{
//Print out return string"
printf("%s\n", ptr);
}
return 0;
}
Output:
Sub string not found
3.) If s2 points to a string with zero length, the function returns s1.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
//Define a pointer of type char, a string and the substring to be found
char *ptr;
char s1[] = "Aticleworld.com";
char s2[] = "";
//Find memory address where s2 "ABC" is found in s1
ptr = strstr(s1, s2);
if(ptr == NULL)
{
//Sub string not found
printf("Sub string not found");
}
else
{
//Print out return string"
printf("%s\n", ptr);
}
return 0;
}
Output:
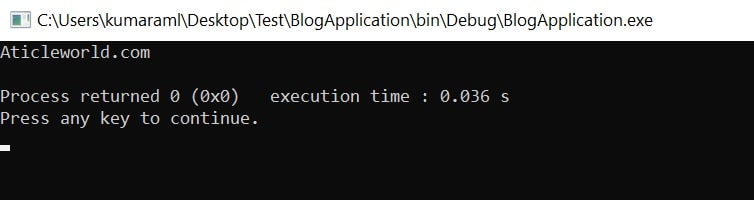
4.) It is the programmer’s responsibility to pass the valid string in the strstr function.
Recommended Articles for you:
- Implement and use of memset of in C
- How to make memcpy function in C
- Implement own memmove in C.
- memmove vs memcpy.
- How to use and implement strcmp in C.
- Implement vector in C.
- How to Use strncpy() and implement own strncpy().
- Implement your own strcat in C.
- How to pass an array as a parameter?
- Implement own atoi in C.
- 10 Best C Programming Books.
- Best mouse for a programmer.
- Dangling, Void, Null and Wild Pointers
- When and how to use array in C?
- Memory Layout in C.
- File handling in C, In a few hours.