In my previous article, I explained the basic concepts of a linked list along with its advantages and disadvantages. In this article, I will show you how to insert a new node into an existing linked list.
Earlier, I shared an example where I created a linked list with four nodes. While that example was useful for understanding how to build a linked list, it wasn’t generic or reusable.
In this article, I’ll create a generic function to insert a new node into an existing linked list, allowing flexibility based on the user’s requirement.
There are three common ways to insert a new node in a linked list:
-
At the beginning of the list
-
After a specific node in the list
-
At the end of the list
Insert a Node at the Beginning of the Linked List in C:
To insert a new node at the beginning of a linked list, follow these simple steps:
🟩👉 Allocate memory for the new node using malloc():
NodePointer pNewNode = malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
🟩👉 Store the data in the newly created node, if memory allocation is successful:
if (pNewNode != NULL)
{
pNewNode->iData = Value;
}
🟩👉 Link the new node to the existing list by setting its pNextNode pointer to the current head node.
if (pNewNode != NULL)
{
pNewNode->pNextNode = head;
}
🟩👉 Update the head pointer to point to the new node:
Head = pNewNode;
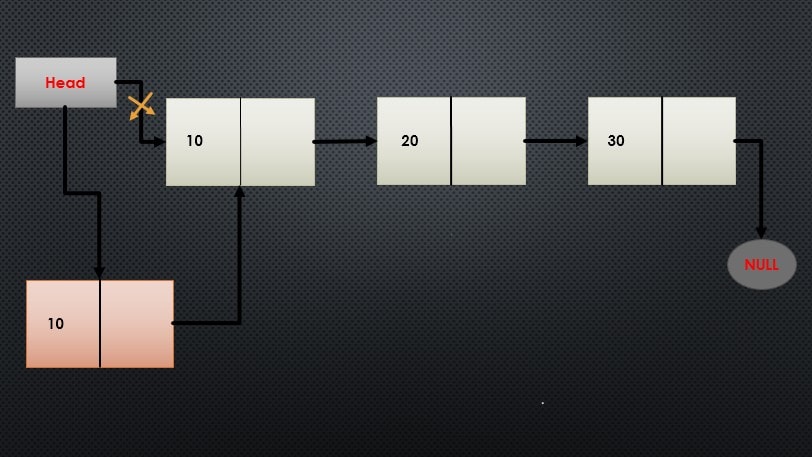
Below is a sample implementation of a function that inserts a new node at the beginning of the linked list:
/**
* @brief Insert a node at the beginning of the list.
*
* @param[in,out] pHead Pointer to head pointer.
* @param[in] value Data to insert.
*
* @return 0 on success, -1 on failure.
*/
int InsertAtBeginning(NodePtr* pHead, int value)
{
int status = -1;
NodePtr newNode = (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (newNode != NULL)
{
newNode->data = value;
newNode->next = *pHead;
*pHead = newNode;
status = 0;
}
return status;
}
Insert a new node after a node:
In a linked list, data is not stored in contiguous memory, so to reach a specific node, we must always start traversing from the head. Below are the steps to insert a new node after a given position in the linked list:
1. Initialize a temporary pointer and assign it the address of the first node (i.e., the head of the list):
NodePointer pTmpNode = head;
2. Traverse the list to reach the node after which you want to insert the new node:
unsigned int count = 1;
// Traverse to the specified position
while ((tempNode != NULL) && (count < position))
{
tempNode = tempNode->pNextNode;
count++;
}
3. Verify the existence of the target node (pTmpNode). If it exists, allocate memory for the new node.
if (pTmpNode != NULL)
{
NodePointer pNewNode = malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
// Here your code
}
4. Store the data in the newly created node, if memory allocation was successful:
if(pNewNode != NULL)
{
pNewNode->iData = Value;
}
5. Link the new node by setting its pNextNode to point to the next node of the temporary node:
pNewNode->pNextNode = pTmpNode->pNextNode;
6. Update the temporary node’s link to point to the newly created node:
pTmpNode->pNextNode = pNewNode;
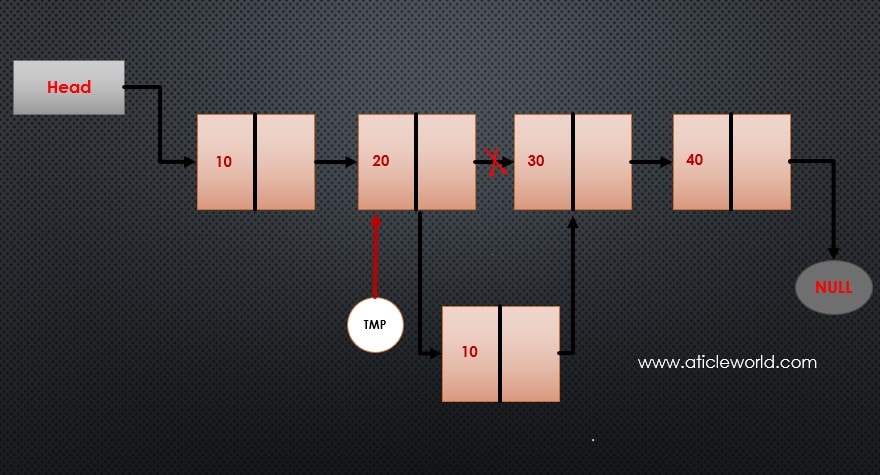
/*
* Inserts a new node with the given data after the specified position in the linked list.
*
* @param pHead Pointer to the head pointer of the linked list
* @param value Data to store in the new node
* @param position Position after which the new node should be inserted (1-based index)
*
* @return 0 on success, -1 on failure
*/
int InsertNodeAfter(NodePointer *pHead, int value, unsigned int position)
{
int retValue = -1;
unsigned int count = 1;
NodePointer tempNode = NULL;
NodePointer newNode = NULL;
// Validate head pointer
if ((pHead != NULL) && (*pHead != NULL))
{
tempNode = *pHead;
// Traverse to the specified position
while (count < position && tempNode != NULL)
{
tempNode = tempNode->pNextNode;
count++;
}
if (tempNode != NULL)
{
// Allocate memory for the new node
newNode = malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
if (newNode != NULL)
{
// Set node data and links
newNode->iData = value;
newNode->pNextNode = tempNode->pNextNode;
tempNode->pNextNode = newNode;
retValue = 0; // success
}
else
{
printf("Memory allocation failed.\n");
}
}
else
{
printf("Invalid position: exceeds list length.\n");
}
}
else
{
printf("Invalid head pointer.\n");
}
return retValue;
}
Insert a Node at the End of the Linked List:
Appending a new node to the end of a linked list is a common operation. Below are the steps to insert a node at the end of an existing linked list:
🔧 Steps to Append a Node:
1. Create a temporary pointer and assign it the address of the first node using the head pointer.
NodePointer pTmpNode = head;
2. Traverse the list to reach the last node (where pNextNode is NULL).
while (pTmpNode->pNextNode != NULL)
{
pTmpNode = pTmpNode->pNextNode;
}
3. Allocate memory dynamically for the new node.
NodePointer pNewNode = malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
4. If memory allocation is successful, assign the user-defined value to the iData field.
if (pNewNode != NULL)
{
pNewNode->iData = value; // replace `value` with actual data
}
5. Link the new node to the list by assigning its address to the pNextNode of the last node.
pTmpNode->pNextNode = pNewNode;
6. Mark the new node as the last node by setting its pNextNode to NULL.
pNewNode->pNextNode = NULL;
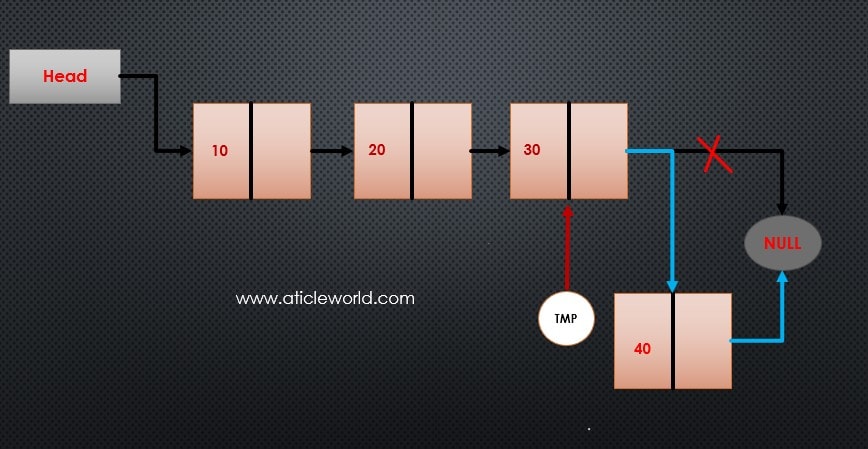
Note: Don’t forget to free the allocated memory.
Free the Allocated memory
/* Paas the reference of the head pointer of a list. This function use
to free the all allocated memory*/
void FreeAllocatedMemory(NodePointer *pHead)
{
NodePointer pTmpNode = NULL;
NodePointer pFirstNode = NULL;
//Assign the Address of first node
pFirstNode = *pHead;
/*check if pFirstNode is NULL, then now list is empty,
so assign NULL to head and return.*/
while (pFirstNode != NULL)
{
/*Save the pFirstNode in a pTmpNode node pointer*/
pTmpNode = pFirstNode ;
/*Assign the address of next on your list*/
pFirstNode = pFirstNode->pNextNode;
//Free the allocated memory
free(pTmpNode );
}
//Assign NULL to the head pointer
*pHead = NULL;
}
In below program, I am creating a linked list where I am adding the node at the beginning, end and at any position of the linked list.
// A simple C program to introduce a linked list
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
// Creating Node
struct Node
{
/*Data field*/
int iData;
/*Node Pointer*/
struct Node *pNextNode;
};
// Define the new type Node type and Node pointer
typedef struct Node NodeType, * NodePointer;
/* Paas the reference of the head pointer of a list and
an integer data. This function use to add the node at the beginning*/
int InsertNodeAtBeginning(NodePointer * pHead, int iUserData)
{
int iRetValue = -1;
// Call malloc to allocate memory in heap for the new node
NodePointer pNewNode = malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
if( pNewNode != NULL) //Check allocated memory
{
pNewNode->iData = iUserData; //put the desire Data
pNewNode->pNextNode = *pHead; //Give the Address of first Node
*pHead = pNewNode; // Assign the Address of New Node to Head
iRetValue = 0; // Update the return value
}
return iRetValue;
}
/* Paas the reference of the tempnode pointer of a list and
an integer data*/
int InsertNodeAfterNode(NodePointer * pHead, int iUserData,unsigned int iPosition)
{
int iRetValue = -1;
NodePointer pTmpNode = NULL;
unsigned int iCount = 0;
//Give the Address of first Node
pTmpNode = *pHead;
for( iCount = 1; ((iCount < iPosition) && (pTmpNode!= NULL)) ; iCount++)
{
pTmpNode = pTmpNode ->pNextNode;
}
/* check the pTmpNode*/
if (pTmpNode == NULL)
{
printf("Enter Position is Invalid\n");
return iRetValue;
}
else
{
/* allocate memory for the new node */
NodePointer pNewNode = malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
if( pNewNode != NULL)
{
//put in the data
pNewNode->iData = iUserData;
//Assign the address of next node to the new node
pNewNode->pNextNode = pTmpNode->pNextNode;
// Assign the address of new node to the previous node
pTmpNode->pNextNode = pNewNode;
iRetValue = 0;
}
}
return iRetValue;
}
/* Paas the reference of the head pointer of a list and
an integer data. This function use to add the node at the End*/
int InsertNodeAtEnd(NodePointer * pHead, int iUserData)
{
int iRetValue = -1;
NodePointer pLastNode = NULL;
NodePointer pNewNode = NULL;
//Give the Address of first Node
pLastNode = *pHead;
// Call malloc to allocate memory in heap for the new node
pNewNode = malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
if( pNewNode != NULL) //Check allocated memory
{
pNewNode->iData = iUserData; //put the desire Data
pNewNode->pNextNode = NULL; //Give the Address of first Node
iRetValue = 0; // Update the return value
}
// If there is no node in beginning
if(pLastNode == NULL)
{
*pHead = pNewNode;
}
else
{
// Find the address of last node
while( pLastNode ->pNextNode != NULL)
{
pLastNode = pLastNode ->pNextNode;
}
// Assign last node address
pLastNode ->pNextNode = pNewNode;
}
return iRetValue;
}
/* Paas the reference of the head pointer of a list. This function use
to free the all allocated memory*/
void FreeAllocatedMemory(NodePointer *pHead)
{
NodePointer pTmpNode = NULL;
NodePointer pFirstNode = NULL;
//Assign the Address of first node
pFirstNode = *pHead;
/*check if pFirstNode is NULL, then now list is empty,
so assign NULL to head and return.*/
while (pFirstNode != NULL)
{
/*Save the pFirstNode in a pTmpNode node pointer*/
pTmpNode = pFirstNode ;
/*Assign the address of next on your list*/
pFirstNode = pFirstNode->pNextNode;
//Free the allocated memory
free(pTmpNode );
}
//Assign NULL to the head pointer
*pHead = NULL;
}
// This function use to prints the data of the list from the begning
//to the given list.
void PrintTheList(NodePointer pNode)
{
//Clear the screen
printf("\nLinked List is: \n\n");
while (pNode != NULL)
{
printf("\n %d\n\n",pNode->iData);
pNode = pNode->pNextNode;
}
system("pause");
}
//Create a linked list of certain number of nodes
int CreateLinkedList(NodePointer *pHead, int iNumberofNode)
{
int iData = 0;
int iRetValue = -1;
int iCount = 0;
for(iCount =0; iCount < iNumberofNode; iCount++)
{
/*Enter desire data*/
printf("\n\nEnter the Data = ");
scanf("%d",&iData);
if((*pHead) == NULL)
{
//Create First Node
iRetValue = InsertNodeAtBeginning(pHead,iData);
}
else
{
//Add the Node at the End
iRetValue = InsertNodeAtEnd(pHead,iData);
}
}
return iRetValue;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main(void)
{
int iChoice = 0;
int iNumberNode =0;
int iData = 0;
int iPosition =0;
/*Start with the empty list */
NodePointer head = NULL;
while(1)
{
//Select the Choice as per the requirements
printf("\n\n\
1: Create the Linked List\n\
2: Display The Linked List\n\
3: Insert Node at the begninig of Linked list\n\
4: Insert Node at the End of Linked List \n\
5: insert Node After a Node \n\
6: terminatethe process \n\n\n");
printf("\n\nenter your choice = ");
scanf("%d",&iChoice);
switch(iChoice)
{
case 1:
printf("\n\nEnter the number of nodes = ");
scanf("%d",&iNumberNode);
CreateLinkedList(&head,iNumberNode);
break;
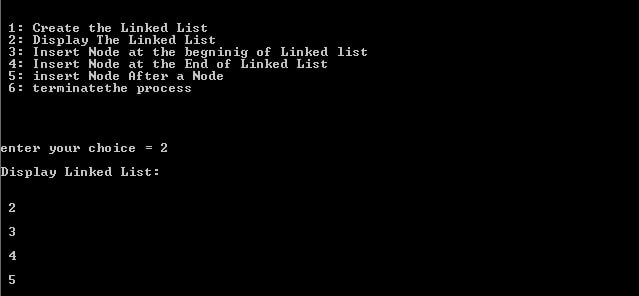
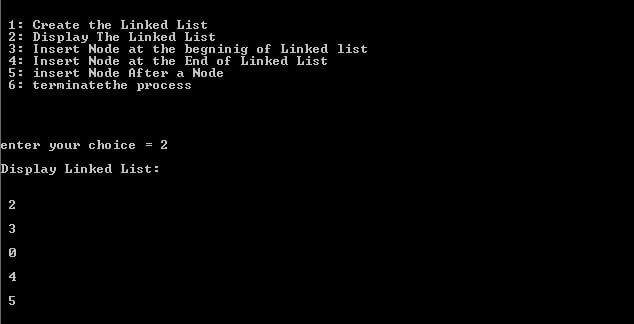
case 2:
PrintTheList(head);
break;
case 3:
printf("\n\nEnter the desired data = ");
scanf("%d",&iData);
InsertNodeAtBeginning(&head,iData);
break;
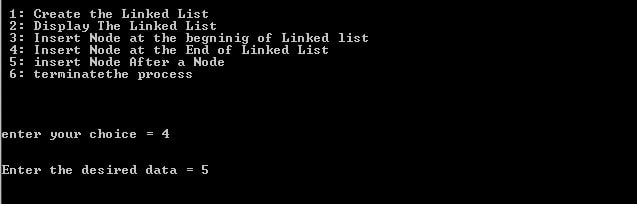
case 4:
printf("\n\nEnter the desired data = ");
scanf("%d",&iData);
InsertNodeAtEnd(&head,iData);
break;
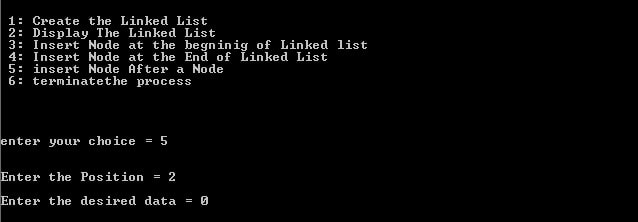
case 5:
printf("\n\nEnter the Position = ");
scanf("%d",&iPosition);
printf("\nEnter the desired data = ");
scanf("%d",&iData);
InsertNodeAfterNode(&head,iData,iPosition);
break;
case 6:
printf("\n\nFree the all Allocated memory\n");
FreeAllocatedMemory(&head);
printf("\n\nprocess is terminated\n ");
exit(1);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
OutPut:
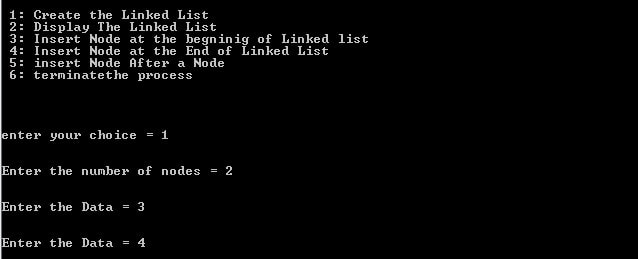
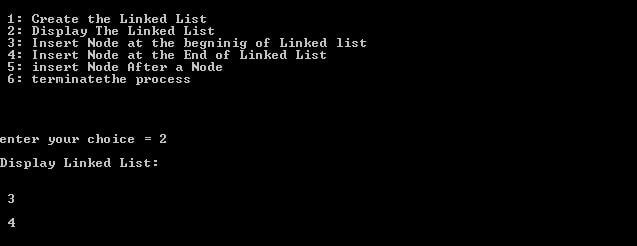
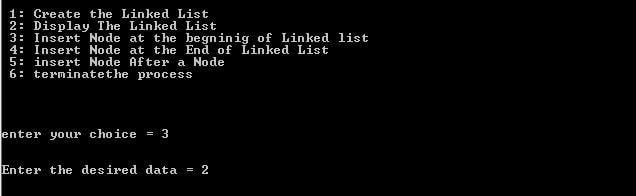
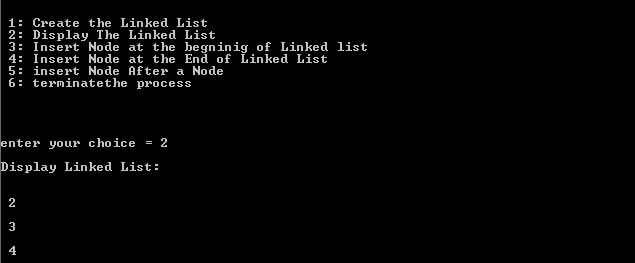
1. Create a linked-list using two nodes.