The isprint function in C programming checks whether a character is a printable character or not. The printable character could be alphanumeric numbers (0 to 9, A to Z, or a to z), a punctuation character(!"#$%&'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\]^_`{|}~), or space ( ' '), or any character classified as printable by the current C locale.
It is declared in ctype.h and takes one argument in the form of integer and returns the value of type int. If the character passed is a printable character, it returns a non-zero integer. If not, it returns 0.
Syntax of isprint function in C:
//Syntax of isprint int isprint(int c);
Parameters:
c => character to classify
Return value:
Non-zero value => If the argument is a printable character.
0 => If the argument is neither a printable character.
Example,
Input : 'a' Output : Non-zero value Input : ';' Output : Non-zero value Input : '\n' Output : Zero
C program to understand the working of isprint function:
Consider the below code where I am passing different characters in the isprint function. You can see the output of this function with different characters.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int main()
{
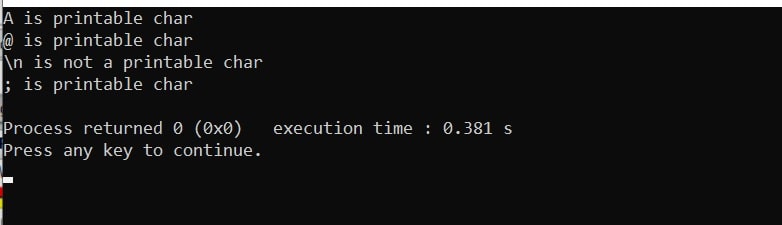
unsigned char c = 'A';;
int result = isprint(c);
result ? printf("A is printable char\n"):printf("A is not a printable char\n");
c = '@';
result = isprint(c);
result ? printf("@ is printable char\n"):printf("@ is not a printable char\n");
c = '\n';
result = isprint(c);
result ? printf("\\n is printable char\n"): printf("\\n is not a printable char\n");
c = ';';
result = isprint(c);
result ? printf("; is printable char\n"): printf("; is not a printable char\n");
return 0;
}
Output:
C Program To Print all Printable characters using the isprint():
Let’s C a C program to print default C printable characters.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int main()
{
unsigned int i;
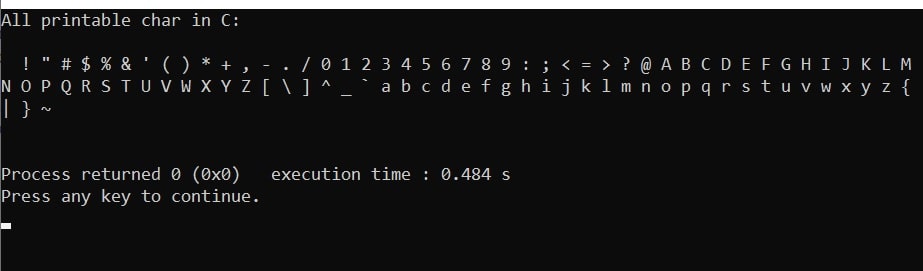
printf("All printable char in C: \n\n");
// looping through all ASCII characters
for (i = 0; i <= 127; ++i)
{
if(isprint(i)!= 0)
{
printf("%c ", i);
}
}
printf("\n\n");
return 0;
}
Output:
Note: If the argument’s value (c) is neither representable as unsigned char not equal to EOF, the behavior of isprint is undefined.
As we know the behavior of isprint is undefined if the argument’s value is neither representable as unsigned char nor equal to EOF. So to use these functions safely with plain chars (or signed chars), the argument should first be converted to unsigned char. Because it is good to convert signed char to unsigned char before being assigned or converted to a larger signed type.
int my_isprint(char ch)
{
return isprint((unsigned char)ch);
}
C Program To Print all characters of a string until not get not Printable characters using the isprint():
The below-mentioned C code prints a string character by character until not get a not printable character. When not printable character met breaks the while-loop. In this code, only the “Aticleworld” would be printed, since the line ends with a newline character (‘\n‘), which is not a printable character.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int main ()
{
int i=0;
char str[]="Aticleworld\n is good website to learn C\n";
while (isprint((unsigned char)str[i]))
{
putchar ((unsigned char)str[i]);
i++;
}
return 0;
}
Output:
Aticleworld
Recommended Post:
- How to use ispunct function in C programming?
- tolower function in C.
- How to use the islower function in C?
- Use of iscntrl function in C.
- How to use isalpha function in C programming?
- Use isalnum function in C programming?
- How to use isdigit function in C programming?
- How to use sizeof operator in C.
- _Alignof or alignof Operator in C
- Alignment specifiers in C ( _Alignas).
- Function Specifiers in C.
- Type qualifiers in C.
- Punctuators in C.
- Elements of C language.