A pointer is an amazing tool of c language we can do any task easily with the help of pointers. In my previous article, we have read that how to calculate the size of structure without using the sizeof() operator.
In this article, I am calculating the sizeof array without using the sizeof() operator. Calculating the size of an array in c without using the sizeof() operator seems to be difficult but with the help of pointers arithmetic, we can do it easily.
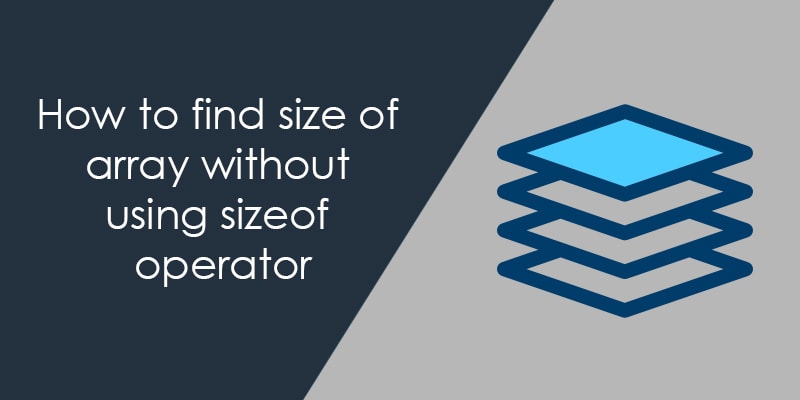
In C language when we increment or decrements the pointer then pointer point the next or previous memory location. The next or previous location depends on the pointer type. If the pfData is a pointer to the float and float size is 4 byte then the next location will be 4 bytes ahead of the current location.
Let us see some example programs where we are calculating the number of elements in the array (size of the array) without knowing the data type of elements.
Example program 1:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int iTotalElement = 0 ;
int aiData[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60};
//Calculate numbers of elements using pointer arithmetic
iTotalElement = *(&aiData + 1) - aiData;
printf("Number of element = %d",iTotalElement);
return 0;
}
Output:
Before understanding the above concept I want to remind the relation between array and pointer.
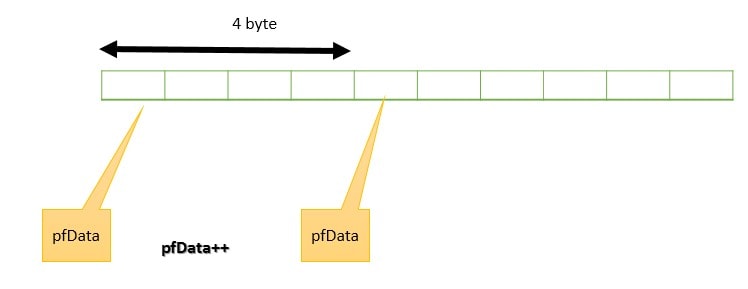
Let’s suppose aiData is an array of integers then &aiData[i] is the pointer to the integer and its value is the address of the ith element. We can also represent the statement in mathematical form.
aiData[i] = *(aiData + i); *(aiData + i) = aiData[i]; (aiData + i) = &aiData[i];
If the value of i is 0.
(aiData + 0) = &aiData[0]; aiData = &aiData[0];
It means an array name is the address of its first element.
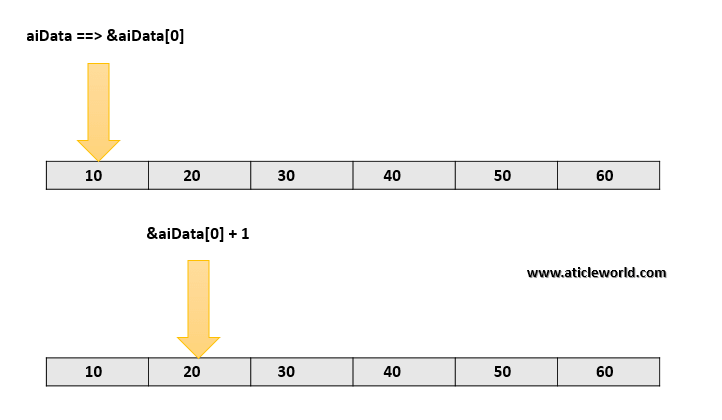
Note: But when you put the ampersand(&) before the array name then its type change. It becomes a pointer to the array.
In the short, we can say.
aiData ====> Pointer to the first element of the array .
&aiData ====> Pointer to an array of 6 elements.
&aiData + 1 ====> Address of next memory block (Address ahead of 6 integers)
*(&aiData+ 1) ====> Dereferencing to *(&aiData + 1) gives the address of first element of second memory block.
*(&aiData+ 1) – aiData ====> Since *(&aiData + 1) points to the address ahead of 6 integers , the difference between two is 6.
Example program 2:
Create own sizeof operator using the macro and calculate the total number of elements in the array.
#include <stdio.h>
// User created size of operator
#define SIZEOF(Var) ((char*)(&Var + 1) -(char*)&Var)
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int iTotalElement = 0 ;
int aiData[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60};
iTotalElement = SIZEOF(aiData)/SIZEOF(aiData[0]);
printf("Number of element = %d",iTotalElement);
return 0;
}
Output:

Recommended Articles for you,
- Calculate the size of structure without the sizeof the operator.
- structure in C: you should know in depth
- structure padding, you should know.
- What is flexible array member in c?
- What is importance of struct hack in c?
- Best structure padding questions.
- How to pass an array as a parameter in C?
- How to access a two-dimensional array using pointers in C?
- Brief Introduction of switch case in C.
- A brief description of the pointer in C.
- Dangling, Void, Null and Wild Pointers
- How to use function pointer in C?
- How to use the structure of function pointer in c language?
- Replace the nested switch case using an array and function pointer.
- Implement state machine in C.
- Function pointer in structure.
- Pointer Arithmetic in C.
- void pointer in C.
- 10 questions about dynamic memory allocation.
- Memory Layout in C.
- 100 C interview Questions
- File handling in C.
- C format specifiers.