In this article, we will learn, how to calculate the length of a linked list using the iterative and recursive method.
Iterative method
An iterative method is the simplest way to calculate the length of the linked list. In the iterative method, we simply take a counter whose initial value is zero. Now we will trace the linked list till the last node using an iteration and increment the counter in each iteration.
STEPS
- Initialize the counter with zero.
- Initialize a node pointer with the head pointer, pTmpNode = head.
- Trace the linked list until not getting the NULL pointer.
pTmpNode = pTmpNode -> pNextNode - Increment counter on each iteration , iCounter ++.
/* This function use to prints the data of the list from the beginning
and get the length of list*/
void GetAndPrintTheList(NodePointer pNode,int *iLengthOfList)
{
int iCounter = 0;
NodePointer pTmpNode = pNode;
printf("\nDisplay Linked List: \n\n");
while (pTmpNode != NULL)
{
printf("\n %d\n",pTmpNode->iData);
pTmpNode = pTmpNode->pNextNode;
//Increment Countr for every itteration
iCounter++;
}
(*iLengthOfList) = iCounter;
printf("\n\n");
}
Driver program to test the above function
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
// Creating Node
struct Node
{
int iData;
struct Node *pNextNode;
};
// Define the new type Node type and Node pointer
typedef struct Node NodeType, * NodePointer;
/* Paas the reference of the head pointer of a list and
an integer data. This function use to add the node at the End*/
int InsertNodeAtEnd(NodePointer * pHead, int iUserData)
{
int iRetValue = -1;
NodePointer pLastNode = NULL;
NodePointer pNewNode = NULL;
//Give the Address of first Node
pLastNode = *pHead;
// Call malloc to allocate memory in heap for the new node
pNewNode = malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
if( pNewNode != NULL) //Check allocated memory
{
pNewNode->iData = iUserData; //put the desire Data
pNewNode->pNextNode = NULL; //Give the Address of first Node
iRetValue = 0; // Update the return value
}
// If there is no node in beginning
if(pLastNode == NULL)
{
*pHead = pNewNode;
}
else
{
// Find the address of last node
while( pLastNode ->pNextNode != NULL)
{
pLastNode = pLastNode ->pNextNode;
}
// Assign last node address
pLastNode ->pNextNode = pNewNode;
}
return iRetValue;
}
/* Paas the reference of the head pointer of a list. This function use
to free the all allocated memory*/
void FreeAllocatedMemory(NodePointer *pHead)
{
NodePointer pTmpNode = NULL;
NodePointer pFirstNode = NULL;
//Assign the Address of first node
pFirstNode = *pHead;
/*check if pFirstNode is NULL, then now list is empty,
so assign NULL to head and return.*/
while (pFirstNode != NULL)
{
/*Save the pFirstNode in a pTmpNode node pointer*/
pTmpNode = pFirstNode ;
/*Assign the address of next on your list*/
pFirstNode = pFirstNode->pNextNode;
//Free the allocated memory
free(pTmpNode );
}
//Assign NULL to the head pointer
*pHead = NULL;
}
/* This function use to prints the data of the list from the beginning
and get the length of list*/
void GetAndPrintTheList(NodePointer pNode,int *iLengthOfList)
{
int iCounter = 0;
NodePointer pTmpNode = pNode;
printf("\nDisplay Linked List: \n\n");
while (pTmpNode != NULL)
{
printf("\n %d\n",pTmpNode->iData);
pTmpNode = pTmpNode->pNextNode;
//Increment Countr for every itteration
iCounter++;
}
(*iLengthOfList) = iCounter;
printf("\n\n");
}
//Create a number of nodes
int CreateLinkedList(NodePointer *pHead, int iNumberofNode)
{
int iData = 0;
int iRetValue = -1;
int iCount = 0;
NodePointer pNewNode = NULL;
for(iCount =0; iCount < iNumberofNode; iCount++)
{
/*Enter desire data*/
printf("\n\nEnter the Data = ");
scanf("%d",&iData);
if((*pHead) == NULL)
{
// Call malloc to allocate memory in heap for the first node
pNewNode = malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
if( pNewNode != NULL) //Check allocated memory
{
pNewNode->iData = iData; //put the desire Data
pNewNode->pNextNode = NULL; //Give the Address of first Node
*pHead = pNewNode; /*Assign the address of
first node to the head pointer*/
iRetValue = 0; // Update the return value
}
}
else
{
//Add the Node at the End
iRetValue = InsertNodeAtEnd(pHead,iData);
}
}
return iRetValue;
}
int main(void)
{
int iNumberNode =0;
int LengthOfList = 0;
/*Start with the empty list */
NodePointer head = NULL;
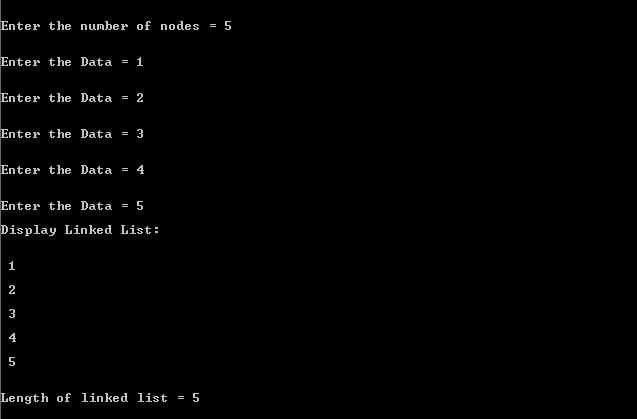
printf("\n\nEnter the number of nodes = ");
scanf("%d",&iNumberNode);
//Create a linked list of three node
CreateLinkedList(&head,iNumberNode);
//Print the created list and get the length
GetAndPrintTheList(head,&LengthOfList);
// Length of Linked List
printf("Length of linked list = %d\n",LengthOfList);
//Free the allocated memory
FreeAllocatedMemory(&head);
return 0;
}
OutPut:
If you want to learn more about the c language, here 10 Free days (up to 200 minutes) C video course for you.
Recursive method
We can also find the length of the linked list using the recursive method. In which we will decrease the node and increase the counter in each recursive call.
Generally, people preferred the iterative method to calculate the length of the list because in the recursive method we are used stack memory in the calculation, if the size of the linked list is too long then might be you faced the stack overflow scenario.
STEPS:
- If the head is NULL, return 0.
- Else return 1 + GetAndPrintTheList(pNode->pNextNode).
/* Counts the no. of nodes */
int GetAndPrintTheList(NodePointer pNode)
{
// Base case
if (pNode == NULL)
return 0;
// count is 1 + count of remaining list
return 1 + GetAndPrintTheList(pNode->pNextNode);
}
Driver program to test the above function
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
// Creating Node
struct Node
{
int iData;
struct Node *pNextNode;
};
// Define the new type Node type and Node pointer
typedef struct Node NodeType, * NodePointer;
/* Paas the reference of the head pointer of a list and
an integer data. This function use to add the node at the End*/
int InsertNodeAtEnd(NodePointer * pHead, int iUserData)
{
int iRetValue = -1;
NodePointer pLastNode = NULL;
NodePointer pNewNode = NULL;
//Give the Address of first Node
pLastNode = *pHead;
// Call malloc to allocate memory in heap for the new node
pNewNode = malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
if( pNewNode != NULL) //Check allocated memory
{
pNewNode->iData = iUserData; //put the desire Data
pNewNode->pNextNode = NULL; //Give the Address of first Node
iRetValue = 0; // Update the return value
}
// If there is no node in beginning
if(pLastNode == NULL)
{
*pHead = pNewNode;
}
else
{
// Find the address of last node
while( pLastNode ->pNextNode != NULL)
{
pLastNode = pLastNode ->pNextNode;
}
// Assign last node address
pLastNode ->pNextNode = pNewNode;
}
return iRetValue;
}
/* Paas the reference of the head pointer of a list. This function use
to free the all allocated memory*/
void FreeAllocatedMemory(NodePointer *pHead)
{
NodePointer pTmpNode = NULL;
NodePointer pFirstNode = NULL;
//Assign the Address of first node
pFirstNode = *pHead;
/*check if pFirstNode is NULL, then now list is empty,
so assign NULL to head and return.*/
while (pFirstNode != NULL)
{
/*Save the pFirstNode in a pTmpNode node pointer*/
pTmpNode = pFirstNode ;
/*Assign the address of next on your list*/
pFirstNode = pFirstNode->pNextNode;
//Free the allocated memory
free(pTmpNode );
}
//Assign NULL to the head pointer
*pHead = NULL;
}
/* Counts the no. of nodes */
int GetAndPrintTheList(NodePointer pNode)
{
// Base case
if (pNode == NULL)
return 0;
// count is 1 + count of remaining list
return 1 + GetAndPrintTheList(pNode->pNextNode);
}
//Create a number of nodes
int CreateLinkedList(NodePointer *pHead, int iNumberofNode)
{
int iData = 0;
int iRetValue = -1;
int iCount = 0;
NodePointer pNewNode = NULL;
for(iCount =0; iCount < iNumberofNode; iCount++)
{
/*Enter desire data*/
printf("\n\nEnter the Data = ");
scanf("%d",&iData);
if((*pHead) == NULL)
{
// Call malloc to allocate memory in heap for the first node
pNewNode = malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
if( pNewNode != NULL) //Check allocated memory
{
pNewNode->iData = iData; //put the desire Data
pNewNode->pNextNode = NULL; //Give the Address of first Node
*pHead = pNewNode; /*Assign the address of
first node to the head pointer*/
iRetValue = 0; // Update the return value
}
}
else
{
//Add the Node at the End
iRetValue = InsertNodeAtEnd(pHead,iData);
}
}
return iRetValue;
}
int main(void)
{
int iNumberNode =0;
int LengthOfList = 0;
/*Start with the empty list */
NodePointer head = NULL;
printf("\n\nEnter the number of nodes = ");
scanf("%d",&iNumberNode);
//Create a linked list of three node
CreateLinkedList(&head,iNumberNode);
//Print the created list and get the length
LengthOfList = GetAndPrintTheList(head);
/*
Linked list passed :1>2->3->4->5->Null ==============|
Linked list passed :2->3->4->5->Null ===========| |
Linked list passed :3->4->5->Null =========| | |
Linked list passed :4->5->Null ========| | | |
Linked list passed :5->Null ======| | | | |
Linked list passed :Null ===| | | | | |
| | | | | |
returned : 0 <===| | | | | |
returned : 1 + Recursive Call <===| | | | |
returned : 1 + Recursive Call <========| | | |
returned : 1 + Recursive Call <============| | |
returned : 1 + Recursive Call <=================| |
returned : 1 + Recursive Call <===================== |
Now Length linked list = 1+1+1+1+1+0
*/
// Length of Linked List
printf("\n\nLength of linked list = %d\n",LengthOfList);
//Free the allocated memory
FreeAllocatedMemory(&head);
return 0;
}
OutPut:

Note: In recursion, you can also use the static variable to find the length of the variable.
/* Counts the no. of nodes */
int GetAndPrintTheList(NodePointer pNode)
{
//static variable
static int iCount =0;
// Base case
if (pNode == NULL)
return iCount;
iCount++;
// Recursive call of function
GetAndPrintTheList(pNode->pNextNode);
}