This blog post explains the importance and use of the “C++ mutable keyword”. You will learn here when and how to use the mutable keyword in C++ programming with some example codes. But before going in depth-first we need to know that mutable is a storage class specifier, like static, thread_local, and extern.
What is the mutable keyword in C++?
The mutable specifier can only be applied to a non-static data member whose type is neither const-qualified nor a reference type. If a data member is declared mutable, then it is legal to assign a value to this data member from a const member function. For example,
class Data
{
mutable const int* ptr1; // OK
mutable int* const ptr2; // ill-formed because ptr2 is const
};
When need to use the mutable keyword?
As we know that we can not modify data members of class/struct through the const method. Let’s see the example code, where I am modifying the value of data member “m_accessCount” in GetData. The GetData is const method.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Data
{
public:
Data():m_accessCount(0)
{
}
int GetData() const //const method
{
return (++m_accessCount);
}
private:
int m_accessCount; //data member
};
int main()
{
Data obj;
cout << obj.GetData()<<endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
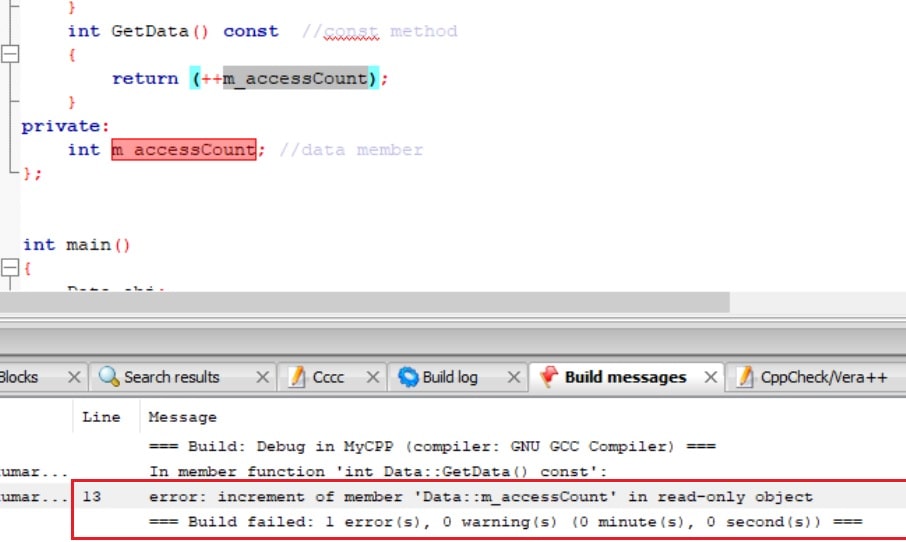
But sometimes we need to modify one or more data members of class/struct through the const method by preventing to modify other data members. This task can be easily performed by using the mutable keyword.
The mutable specifier on a class data member nullifies a const specifier applied to the containing class/struct object and permits modification of the mutable class member even though the rest of the object is const.
Let’s consider the same above discussed example but I am using a mutable keyword with m_accessCount.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Data
{
public:
Data():m_accessCount(0)
{
}
int GetData() const //const method
{
return (++m_accessCount);
}
private:
mutable int m_accessCount; //data member with mutable
};
int main()
{
Data obj;
cout << obj.GetData()<<endl;
return 0;
}
Output: 1
What will happens if try to modify a non-mutable data member with a const object?
Except that any class member declared mutable can be modified, any attempt to modify a const object during its lifetime results in undefined behavior. Let’s see some example codes to understand this statement.
Example 1:
In the below example, const object “y” tries to modify the mutable and non-mutable data member. We will get here compiler error because we can not modify the non-mutable data member with const object.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class X
{
public:
X() {}
//mutable member
mutable int i;
int j;
};
class Y
{
public:
//object of x
X x;
Y():x()
{
}
};
int main()
{
const Y y;
y.x.i++; // well-formed: mutable member can be modified
y.x.j++; // ill-formed: const-qualified member modified
return 0;
}
Output:
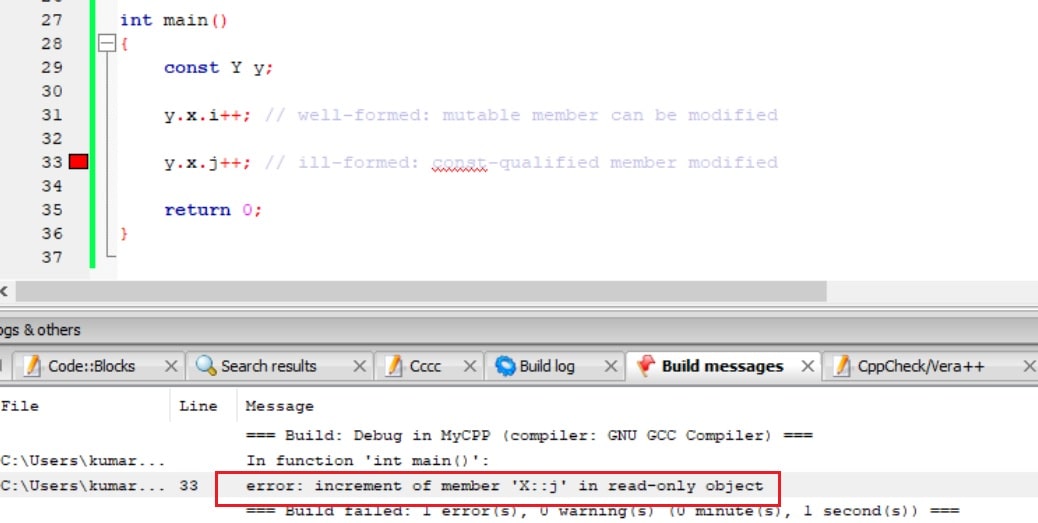
Example 2:
In the below example forcefully we are trying to change the value of non-mutable data members through a const object. In that situation, we will get undefined behavior. Let’s see the example code,
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class X
{
public:
X() {}
//mutable member
mutable int i;
int j;
};
class Y
{
public:
//object of x
X x;
Y():x()
{
}
};
int main()
{
const Y y;
Y* p = const_cast<Y*>(&y); // cast away const-ness of y
p->x.i = 99; // well-formed: mutable member can be modified
p->x.j = 99; // undefined: modifies a const subobject
return 0;
}
Output:
The behavior of the code will be undefined.
Recommended Articles for you:
- Amazing list of Gifts for Programmers, You must.
- Introduction of reference in C++.
- Use of explicit keyword in C++.
- Best electronic kits for programmers.
- References and const in C++ with example programs.
- C++ Interview Questions with Answers.
- constructors in c++.
- Interview questions on constructor and destructor in C++.
- C++ Variables, Constants, and literals.
- Interview questions on the virtual keyword in C++.
- Interview Questions on Inheritance in C++.
- 100 embedded C interview Questions.
- Python Interview Questions with Answer.
- 100 c interview questions, your interviewer might ask.
- C Interview Questions for the experience
