In this blog post, you will learn to print Twin prime numbers between two ranges (entered by the user). Before writing the code I think first we need to understand the Twin prime numbers.
What is Twin Primes Numbers?
A twin prime is a prime number that is either 2 less or 2 more than another prime number—for example, The first few twin prime pairs are :
(3, 5), (5, 7), (11, 13), (17, 19), (29, 31), (41, 43), (59, 61), (71, 73), (101, 103), (107, 109), (137, 139), ..etc
Note: Usually the pair (2, 3) is not considered to be a pair of twin primes.
C program to print Twin prime numbers between two ranges:
To understand this C program, you should have the knowledge of the following C programming topics:
Now it’s time to write the program to print Twin prime numbers between two ranges.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
//function to check prime number
int isPrimeNumber(int num)
{
int i = 0,flag = 1;
if(num <= 1)
{
flag = 0;
}
else
{
for(i = 2; i <= (num/2); i++)
{
if((num % i) == 0) // Check prime num
{
flag = 0;
break;
}
}
}
return flag;
}
int main()
{
int num1, num2,i, isTwinPrimePresent = 0;
printf("Enter num1: ");
scanf("%d", &num1);
printf("Enter num2: ");
scanf("%d", &num2);
for(i = num1; i < num2; ++i)
{
if(isPrimeNumber(i) && isPrimeNumber(i+2))
{
printf("{%d, %d}\n", i, i+2);
isTwinPrimePresent = !isTwinPrimePresent?1:isTwinPrimePresent;
}
}
if(!isTwinPrimePresent)
{
printf("Twin Prime not found\n");
}
return 0;
}
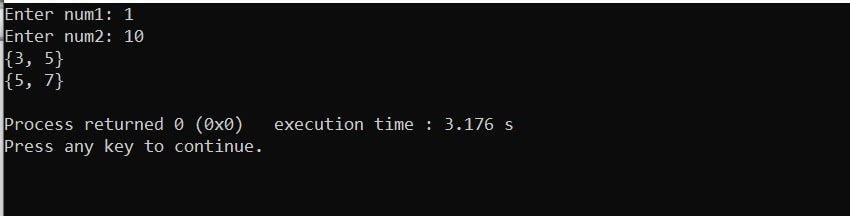
Output 1:
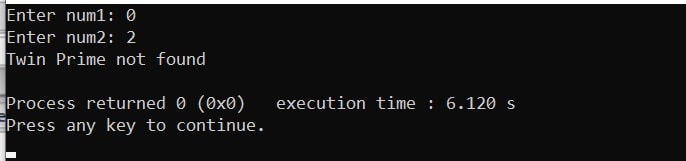
Output 2:
How it works:
In line 38, we have a for loop that iterates over the numbers between the specified range.
In line 40, we are calling the isPrimeNumber() function to check the prime number. We are checking numbers ‘i’ and ‘i’+2 with isPrimeNumber().
If the condition satisfies then numbers ‘i’ and ‘i’ + 2 are twin primes. In line 43, we are maintaining a variable that will print a message if Twinprime not available in the given range.
Using Sieve of Eratosthenes algorithm:
Using the Sieve of Eratosthenes algorithm we can also print Twin prime numbers between 1 to N (Given number). If you want you can check the article “Find prime numbers up to n using Sieve of Eratosthenes algorithm“.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void printTwinPrime(int n)
{
int isTwinPrimePresent = 0;
if(n <= 1)
{
printf("Enter valid number\n");
}
else
{
// Create a int array "prime[0..n]"
//supported by C99 and above.
//If you want you can create dynamic array.
unsigned char prime[n + 1];
int p = 2;
//Set pcRangePrimeNum 1 from pcRangePrimeNum[0..n]
memset(prime, 1, sizeof(prime));
for (p = 2; (p * p) <= n; p++)
{
// If prime[p] is not changed,
// then it is a prime
if (prime[p] == 1)
{
int i =0;
// Update all multiples of p
for (i = (p * 2); i <= n; i += p)
{
prime[i] = 0;
}
}
}
// to check for twin prime numbers
// display the twin primes
for (p = 2; p <= (n - 2); p++)
{
if (prime[p] && prime[p + 2])
{
printf("{%d, %d}\n", p, p+2);
isTwinPrimePresent = !isTwinPrimePresent?1:isTwinPrimePresent;
}
}
//print message if TwinPrime number not found
if(!isTwinPrimePresent)
{
printf("Twin Prime not found\n");
}
}
}
int main()
{
int num;
printf("Enter num: ");
scanf("%d", &num);
// Calling the function
// to print TwinPrime number if available
printTwinPrime(num);
return 0;
}
Recommended Articles for you:
- Find the prime number using the C program.
- find all prime numbers up to n using trial division and Sieve of Eratosthenes algorithm.
- Check date validity in C?
- Create an employee record system in C.
- Way to create a library management system in C.
- How to create student record system in C?
- Best keyboards for programmers.