In this blog post, we learn how to write a C program to find the count of even and odd elements in the array? So here will write the C program to find the count of even and odd elements in the array. We will also see how to display the count of even and odd elements in the array.
So let’s see the logic to count the even and odd numbers in the given array. Suppose arr is an integer array of size N (arr[N] ), the task is to write the C program to find the count of even and odd elements in the array.
Examples,
//Input array
Input: int arr[5] = {0, 8, 4, 5, 6};
Output:
Number of even elements = 4
Number of odd elements = 1
//Input array
Input: int arr[5] = {11, 32, 13, 52, 62};
Output:
Number of even elements = 3
Number of odd elements = 2
If you want to learn more about the c language, here 10 Free days (up to 200 minutes) C video course for you.
You can check articles,
- C program to find even and odd numbers.
- C Program to Print Even Numbers from 1 to N.
- C Program to find the sum of even numbers from 1 to n.
- C Program to Print Odd Numbers from 1 to N.
Logic to count of even and odd elements in the array with the mathematical expression:
1. Create two intermediate variables evenNumCount and oddNumCount.
2. Initialize the variables ‘evenNumCount ’ and oddNumCount with 0.
3. To find the count of even and odd numbers, iterate through each element.
4. If the element is divisible by 2 ( a[i] % 2 == 0 ), increase the even count otherwise odd count. Here ‘i’ is the ith index of the array. It would be from 0 to N-1. N is the size of the array.
C Program to find the count of even and odd elements in the array using the mathematical expression:
#include <stdio.h>
//Calculate array size
#define ARRAY_SIZE(a) sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0])
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
// variables to store even or odd count
int evenNumCount = 0, oddNumCount = 0;
int i; //for looping
//calculate array size
const int N = ARRAY_SIZE(arr);
// iterate over the arrays
for( i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// check for even number
if(arr[i] % 2 == 0)
{
evenNumCount++;
}
else
{
oddNumCount++;
}
}
printf("Even elements = %d\n", evenNumCount);
printf("Odd elements = %d", oddNumCount);
return 0;
}
Output:
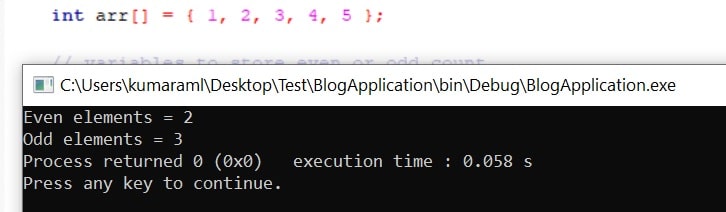
Logic to count of even and odd elements in the array using binary operation:
1. Create two intermediate variables evenNumCount and oddNumCount.
2. Initialize the variables ‘evenNumCount ’ and oddNumCount with 0.
3. To find the count of even and odd numbers, iterate through each element.
4. By doing AND of 1 and that digit ( a[i] & 1 ), if the result comes out to be 0 then the number is even and increases the even count otherwise odd count. Here ‘i’ is the ith index of the array. It would be from 0 to N-1. N is the size of the array.
C Program to find the count of even and odd elements in the array using the binary operation:
#include <stdio.h>
//Calculate array size
#define ARRAY_SIZE(a) sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0])
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
// variables to store even or odd count
int evenNumCount = 0, oddNumCount = 0;
int i; //for looping
//calculate array size
const int N = ARRAY_SIZE(arr);
// iterate over the arrays
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// check for even number
if ((arr[i] & 1) == 0)
{
evenNumCount++;
}
else
{
oddNumCount++;
}
}
printf("Even elements = %d\n", evenNumCount);
printf("Odd elements = %d", oddNumCount);
return 0;
}
Output:

Recommended Articles for you:
- Best gift for programmers.
- Best electronic kits for programmers.
- Write C program to find the sum of array elements.
- Find the sum of array elements using recursion
- C Program to reverse the elements of an array
- C Program to find the maximum and minimum element in the array
- Calculate size of an array in without using sizeof in C
- How to create a dynamic array in C?
- How to access 2d array in C?
- A brief description of the pointer in C.
- Dangling, Void, Null and Wild Pointers
- Function pointer in c, a detailed guide
- How to use the structure of function pointer in c language?
- Memory Layout in C.
- 100 C interview Questions
- File handling in C.
- C format specifiers.