Bit manipulation is one of the most powerful concepts in C programming, C++ programming, and embedded systems development. It allows you to directly access and modify individual bits inside an integer, making it extremely useful for hardware register control, memory optimization, cryptography, networking, and performance-critical applications.
Instead of working on an entire integer, bit manipulation gives you fine-grained control to set, clear, check, or toggle a single bit. This skill is not only essential in embedded firmware and device drivers but also frequently appears in technical interviews.
In this article, we will cover step-by-step how to perform bit operations using functions and macros, along with practical examples that you can apply in real projects.
In this comprehensive guide, you will learn:
- What the N-th bit means in C.
- How to set, clear, check, and toggle a bit using functions and macros.
- Real-world examples and explanations.
- Best practices and common mistakes to avoid.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Bit Manipulation
- How to Set a Bit
- Understanding the N-th Bit
- Setting the N-th Bit in C
- Clearing the N-th Bit in C
- Checking the N-th Bit in C
- Toggling the N-th Bit in C
- Real-World Applications of Bit Manipulation
- Common Mistakes in Bitwise Operations
Note: Quiz on bit-wise operators.
Introduction to Bit Manipulation:
In C, numbers are stored in binary form (a series of 0s and 1s). Sometimes, we don’t want to operate on the whole number but only on specific bits.
For example:
- Turning ON an LED connected to bit-3 of a port register.
- Checking if a flag bit is set in a status register.
- Clearing specific control bits in a configuration register
This is where bit manipulation comes in.
👉 To do this, we use bitwise operators:
| (OR)→ Set bit& (AND)→ Clear or check bit^ (XOR)→ Toggle bit~ (NOT)→ Invert bits
Understanding the N-th Bit:
The N-th bit refers to a bit at position N, starting from 0 (least significant bit, LSB).
When working with registers or variables at the bit level, it is important to remember that bit positions start from 0.
- The least significant bit (LSB) is at position 0.
- The most significant bit (MSB) depends on the size of the register. For an 8-bit register, the MSB is at position 7.
So, if we say “2nd position”, it actually refers to the third bit in the sequence because we begin counting from zero.
Example: 8-bit Register Layout:
The table below shows how the bit positions (indices) map to the bit names (D7 … D0) in an 8-bit register:
| Bit Position | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Bit Name | D7 (MSB) | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 (LSB) |
- Bit 0 (D0) → Least Significant Bit (LSB)
- Bit 7 (D7) → Most Significant Bit (MSB)
If you want to set the 2nd bit, you are actually modifying D2, which corresponds to position 2 (counting from zero).
Setting N-th Bit
Setting a bit means forcing it to 1, regardless of its current value.
When we talk about setting the N-th bit of a number:
- If the bit at position N is already 1, it stays 1.
- If the bit at position N is 0, it changes to 1.
In C and C++, we use the bitwise OR (|) operator to perform this operation.
As we know, the bitwise OR (|) operator evaluates a new integer in which each bit position becomes 1 if either of the operands has a 1 in that position. This property makes it ideal for setting bits.
How It Works?
The bitwise OR compares two numbers at the bit level:
- If either bit is 1, the result is 1.
- If both bits are 0, the result is 0.
So, when we OR a number with a mask that has a 1 at the N-th position, the N-th bit of that number will always be set to 1.
That means, 0 | 0 = 0 1 | 0 = 1 0 | 1 = 1 1 | 1 = 1
Algorithm to set the bits:
Number | = (1UL << nth Position);
This ensures that the bit at position pos is set to 1, while other bits remain unchanged.
Method1: Set nth- bit in C using the function:
#include <stdio.h>
//function to set bit
int setBit(unsigned int data,unsigned int pos)
{
return (data|(1 << pos));
}
int main()
{
unsigned int cData=0x00;
unsigned int pos =0;
printf("cData = 0x%x\n\n",cData);
//Get position from the user
printf("Enter the position which you want set = ");
scanf("%u",&pos);
//Call function to set the bit
cData = setBit(cData,pos);
//Print the data
printf("\n\n%dth Bit Set Now cData will be = 0x%x\n",pos,cData);
return 0;
}
OutPut:
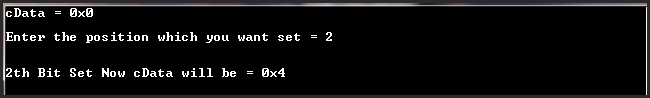
Explanation:
0 is represented as 0 in binary and has its D2 bit(third bit) 0, so setting it will result in 100 i.e. 4.
Method2: Set nth- bit in C using macro
#include <stdio.h>
//Macro to set nth-bit
#define SET_BIT(value, pos) (value |= (1U<< pos))
int main()
{
//value
unsigned int value =0;
//bit position
unsigned int pos = 0;
printf("Enter the value = ");
scanf("%u",&value);
printf("Enter the position you want to Set = ");
scanf("%u",&pos);
//Calling Macro to set nth-bit
printf("After setting nth-bit value will be = %d\n",SET_BIT(value,pos));
return 0;
}
OutPut:
Enter the value = 5
Enter the position you want to Set = 0
After setting nth-bit value will be = 5
Explanation:
5 is represented as 101 in binary and has its first bit 1. So after setting the 0th position, it will result in 101 i.e. 5.
Clearing a Bit
Clearing a bit means forcing it to 0, no matter what its current value is.
When we talk about clearing the N-th bit of a number:
- If the bit at position N is 1, it becomes 0.
- If the bit at position N is already 0, it remains unchanged.
In C and C++, this is done using the bitwise AND (&) operator together with a bit mask.
As we know, the bitwise AND (&) operator evaluates a new integer in which each bit position is 1 only if both operands have 1 in that position. This property makes it perfect for clearing bits when combined with a mask.
How It Works:
The bitwise AND (&) operator compares two numbers at the bit level:
- If both bits are 1, the result is 1.
- If any bit is 0, the result is 0.
To clear a bit, we first create a mask with all bits set to 1 except the N-th bit, which is 0.
- Then, when we AND the number with this mask, the N-th bit is forced to 0.
- All other bits remain unchanged because 1 & x = x.
That means, 0 & 0 = 0 1 & 0 = 0 0 & 1 = 0 1 & 1 = 1
Algorithm to clear the bit:
To clear the nth bit, first, you need to invert the string of bits then AND it with the number.
Number &= ~(1UL << nth Position);
- 1 << N → creates a mask with only the N-th bit set.
- ~(1 << N) → inverts the mask so the N-th bit is 0 and all other bits are 1.
- & → clears the N-th bit while leaving all other bits unchanged.
Method1: Clear nth- bit in C using the function:
#include <stdio.h>
//function to clear nth-bit
int clearNthBit(unsigned int data,unsigned int pos)
{
return (data & (~(1 << pos)));
}
int main()
{
unsigned int cData=0xFF;
unsigned int pos =0;
printf("Initially cData = 0x%x\n\n",cData);
printf("Enter the position which you want clear = ");
scanf("%u",&pos);
//clear the nth bit.
cData = clearNthBit(cData,pos);
//Print the data
printf("\n\n%uth Bit clear Now cData will be = 0x%x\n",pos,cData);
return 0;
}
OutPut:
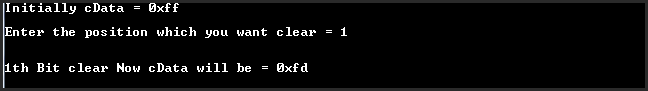
Explanation:
Clearing of D1 bit of 0XFF will give 0XFD.
Method2: Clear nth- bit in C using the macro:
#include <stdio.h>
//Macro to clear nth-bit
#define CLEAR_BIT(value, pos) (value &= (~(1U<< pos)))
int main()
{
unsigned int cData=0xFF;
unsigned int pos =0;
printf("Initially cData = 0x%x\n\n",cData);
printf("Enter the position which you want clear = ");
scanf("%u",&pos);
//Calling macro to clear nth-bit
printf("After clearing nth-bit cData will be = 0x%x\n",CLEAR_BIT(cData,pos));
return 0;
}
Output:
Initially cData = 0xff
Enter the position which you want clear = 0
After clearing nth-bit cData will be = 0xfe
Checking a Bit
Checking a bit means determining whether a specific bit is set (1) or clear (0) in a number.
- If the bit at position N is 1, it is set.
- If the bit at position N is 0, it is clear.
In C and C++, we use the bitwise AND (&) operator to check the value of a bit.
An algorithm to check the bit
if (number & (1 << N))
{
// N-th bit is set
}
else
{
// N-th bit is clear
}
- 1 << N → creates a mask with only the N-th bit set.
- & → isolates the N-th bit of number.
- If the result is non-zero, the bit is set; otherwise, it is clear.
How It Works:
The bitwise AND compares two numbers at the bit level:
- If both bits are 1, the result is 1.
- If either bit is 0, the result is 0.
By creating a mask with only the N-th bit set and ANDing it with the number, we can test if that bit is 1 or 0.
Method1: Check nth- bit in C using the function
#include <stdio.h>
#define SET 1
#define NOT_SET 0
//function to check nth bit
int isNthBitSet(unsigned int data,unsigned int pos)
{
return ((data & (1 << pos))? SET : NOT_SET);
}
int main()
{
//Given data
unsigned int cData=0xFc;
unsigned int pos =0;
unsigned int isBitSet = 0;
printf("Initially cData = 0x%x\n\n",cData);
printf("Enter the position which you want check = ");
scanf("%u",&pos);
//Check bit set or not
isBitSet = isNthBitSet(cData,pos);
if(isBitSet)
{
printf("\nBit is One\n");
}
else
{
printf("\nBit is zero\n");
}
return 0;
}
OutPut 1:
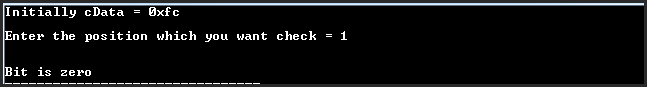
OutPut 2:
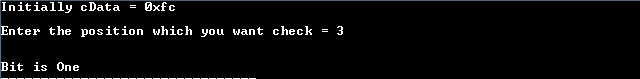
Method2: Check nth- bit in C using macro
#include <stdio.h>
//Macro to check nth-bit
#define IS_BIT_SET(value, pos) (value & (1U<< pos))
int main()
{
//Given data
unsigned int cData=0xFc;
unsigned int pos =0;
printf("Initially cData = 0x%x\n\n",cData);
printf("Enter the position which you want check = ");
scanf("%u",&pos);
//Macro to check nth bit
if(IS_BIT_SET(cData,pos))
{
printf("\n\nBit is One");
}
else
{
printf("\n\nBit is zero");
}
return 0;
}
Toggling a Bit
Toggling a bit means flipping its state:
- If the N-th bit is 1, it changes to 0.
- If the N-th bit is 0, it changes to 1.
In C and C++, we use the bitwise XOR (^) operator to toggle a bit.
To toggle the N-th bit, we create a mask by shifting 1 to the left by N positions and then apply the XOR operator.
How It Works?
The bitwise XOR compares two numbers at the bit level:
- If the two bits are different, the result is 1.
- If the two bits are the same, the result is 0.
That means, 0 ^ 0 = 0 1 ^ 0 = 1 0 ^ 1 = 1 1 ^ 1 = 0
An algorithm to toggle the bits
When we XOR a number with a mask that has a 1 at the N-th position:
- If the bit was 1, it becomes 0.
- If the bit was 0, it becomes 1.
Number ^= (1UL << nth Position);
A simple program to toggle a bit
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
unsigned int cData=0xF8;
int pos =0;
system("COLOR F");
printf("Initially cData = 0x%x\n\n",cData);
printf("Enter the position which you want toggle = ");
scanf("%u",&pos);
//toggle the nth bit.
cData^=1<<pos;
//Print the data
printf("\n\n%uth Bit Set Now cData will be = 0x%x\n",pos,cData);
return 0;
}
Output:
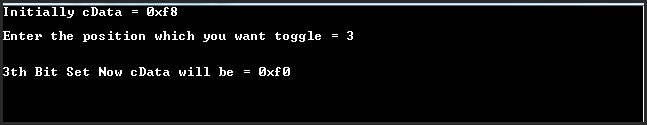
OutPut 2:
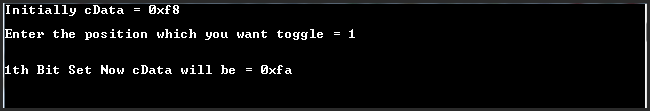
Common Mistakes in Bitwise Operations:
Bitwise operations in C and C++ are simple but easy to misuse. Here are some common mistakes developers often make.
1. Confusing Bit Positions with Bit Masks
Mistake: Writing number | 3 when you intend to set the 3rd bit.
- Issue: 3 is not the 3rd bit; it’s a mask with the first and second bits set (0000 0011).
- Correct Way: Use a mask by shifting 1 to the required bit position:
number |= (1 << 3);// Set 3rd bit
2. Forgetting Operator Precedence:
- Mistake: Writing
if (number & 1 << 3) {}and expecting it to check the 3rd bit.
- Issue: << has higher precedence than &, so it evaluates as
number & (1 << 3). While this may work as expected, it’s unclear and error prone. - Correct Way: Always use parentheses for clarity:
if ((number & (1 << 3)) != 0) {}
3. Using Signed Integers for Bitwise Operations
- Mistake: Performing bit shifts on signed integers (like int).
- Issue: Shifting negative numbers or shifting into the sign bit is undefined behavior in C/C++.
- Correct Way: Use unsigned types (unsigned int, uint32_t) for bitwise operations.
uint32_t mask = 1U << 31;// Safe way to set the 31st bit
4. Off-by-One Errors in Bit Indexing
- Mistake: Thinking the “1st bit” is at position 1.
- Issue: Bit positions are zero-based. The least significant bit (LSB) is at position 0.
- Correct Way: To set the 1st bit (LSB), write:
number |= (1 << 0);// Correct, sets LSB
5. Forgetting to Use Unsigned Literal Suffix
- Mistake: Writing 1 << 31 on a 32-bit signed int.
- Issue: This may invoke undefined behavior due to signed overflow.
- Correct Way: Add U to make the constant unsigned:
uint32_t mask = 1U << 31;
Note: Always use uint32_t (from <stdint.h>) or other fixed-width unsigned types when dealing with bitwise operations. It makes the intent clear, avoids undefined behavior, and improves portability.
Recommended Post for You
- Interview questions on bitwise operators in C
- Operator Precedence And Associativity In C.
- Operators in c language
- C format specifiers.
- Structure padding and data alignment in C.
- Can protocol interview Questions.
- 100 C interview Questions.
- 100 embedded C interview Questions.
- File handling in C.
- Pointer in C.
- C format specifiers.
- Little-endian vs Big Endian.
Your opinion matters
Although here I have tried to puts a lot of points regarding the bit operators but I want to know your opinion on the binary operators, so please don’t forget to write a comment in the comment box.
