Factorial is used in many areas of mathematics but mainly used in permutation and combination. Factorial is the product of the all positive number from 1 to n (user entered number). In simple words, we can say that factorial of n would be 1*2*3*…..*n.
Note: There is no factorial exist for the negative number and the value of !0 is 1.
Factorial of positive number would be:
!n = n * !(n-1)
For example,
!5 = 5*4*3*2*1*!0 = 120.
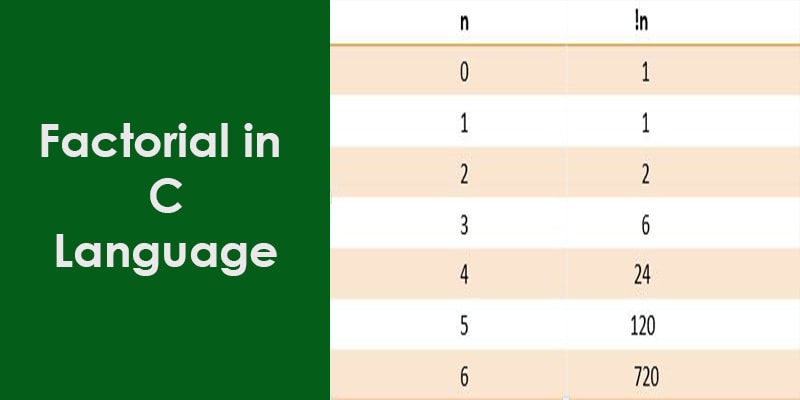
Some factorials of numbers
| n | n! |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 6 |
| 4 | 24 |
| 5 | 120 |
| 6 | 720 |
| 7 | 5040 |
| 8 | 40320 |
| 9 | 362880 |
| 10 | 3628800 |
Here I am describing the few methods to calculate the factorial of a positive number in C. I hope you are familiar with while and for loop in C.
1) Factorial of a number in C using the for loop
The below program takes a positive integer number from the user and computes its factorial using the for loop.
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
unsigned int iLoop,iFactorial = 1;
int iNumber=0;
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%d",&iNumber);
if(iNumber < 0 )
{
printf("factorial of negative number dose not exist\n\n\n");
}
else
{
for(iLoop=1; iLoop<=iNumber; iLoop++)
{
iFactorial*= iLoop;
}
printf("\n\nFactorial of %d is: %u\n\n\n\n",iNumber,iFactorial);
}
return 0;
}
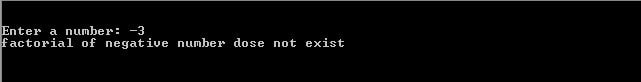
OutPut
When the user Enters the negative number.
When the user enters the positive number.

2.) Factorial of a number using the recursive method.
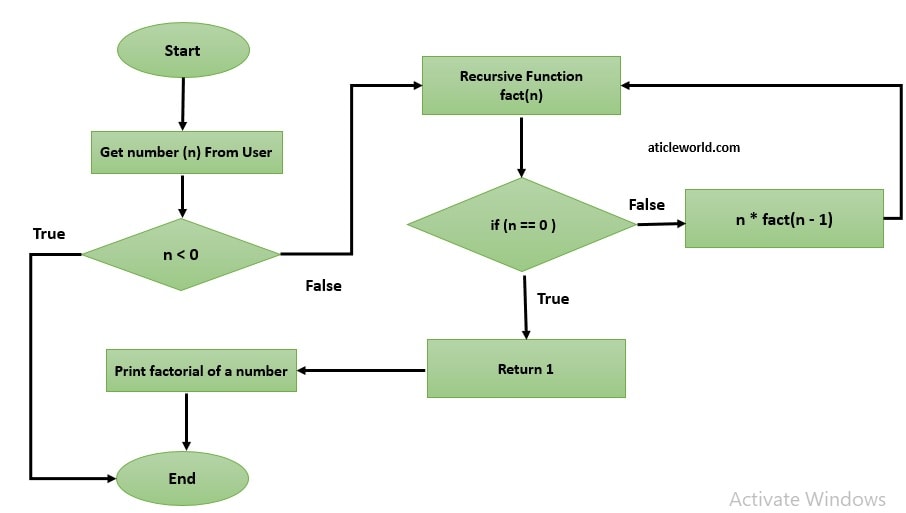
A function is called recursive, if it is called by itself. You can see this article, Recursion in C. Before writing the code I want to show here a flow diagram which to describe the flow of the code.
#include <stdio.h>
//Calculate factorial in C
unsigned long fact(unsigned long int n)
{
if (n == 0)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return(n * fact(n - 1));
}
}
//Driving function
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
unsigned long n = 0;
unsigned result = 0;
printf("Enter a positive integer number: ");
scanf("%lu", &n);
//check negative number
if (n < 0)
{
printf("\nFactorial of a negative number dose not exist \n");
}
else
{
result = fact(n);
printf("\nThe Factorial of %d is : %d.\n", n, result);
}
return 0;
}
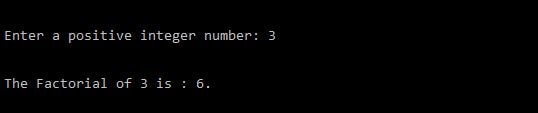
Output:
Working of the above code,
Here n = 3
fact(3) = 3 * fact(2)
fact(2) = 2* fact(1)
fact(1) = 1 *fact(0);
When n=0, condition becomes true and recursion stops and control returns to factorial(1). Now reverse process occurs and function will return a value to the previous function calls.
Note: There should be a termination point in a recursive function.
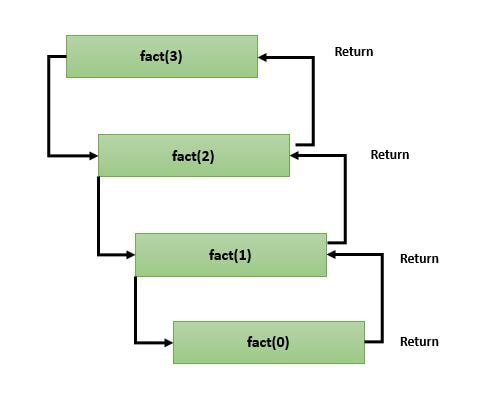
So the final result will be:
fact(3) = 3*2*1 = 6
You can also see the below articles,
3.) Factorial of a number in C using the while loop
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
unsigned int iLoop = 1,iFactorial = 1;
int iNumber = 0;
printf("\n\nEnter a number: ");
scanf("%d",&iNumber);
if(iNumber < 0 )
{
printf("factorial of negative number dose not exist\n\n\n");
}
else
{
while(iLoop <= iNumber)
{
iFactorial*= iLoop; // product from 1 to n
iLoop++; // Increment the value
}
printf("\n\nFactorial of %d is: %u\n\n\n\n",iNumber,iFactorial);
}
return 0;
}
4.) Calculate the factorial using the look-up table
If you need the factorial of the small number then the look-up table is the best option because it is fast as compared to iteration and recursion method.
In below program, I am creating a look-up table which contains the factorial of-of 0 to 10;
#include <stdio.h>
//Function returns the factorial
int iReturnFactorial(int index);
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
long int iFactorial =1;
int iNumber = 0;
printf("Enter a positive integer number: ");
scanf("%d", &iNumber);
if (iNumber < 0)
{
printf("\nFactorial of a negative number dose not exist \n");
}
else
{
iFactorial = iReturnFactorial(iNumber);
printf("\nThe Factorial of %d is : %lu\n", iNumber, iFactorial);
}
return 0;
}
int iReturnFactorial(int index)
{
//Look up table
const int acFactValue [11]= {1,1,2,6,24,120,720,5040,40320,362880,3628800};
return acFactValue[index];
}
5.) Calculate the factorial using a function
#include <stdio.h>
//Function calculate factorial
int iCalculateFactorial(int);
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int iFactorial =1,iNumber=0;
printf("Enter a positive integer number: ");
scanf("%d", &iNumber);
if (iNumber < 0)
{
printf("\nFactorial of a negative number dose not exist \n");
}
else
{
iFactorial = iCalculateFactorial(iNumber);
printf("\nThe Factorial of %d is : %d \n", iNumber, iFactorial);
}
return 0;
}
int iCalculateFactorial(int iNumber)
{
int iLoop, iFactorial = 1;
for(iLoop=1; iLoop<=iNumber; iLoop++)
{
iFactorial*= iLoop;
}
return iFactorial;
}
Recommended Articles for you:
- C program to find a neon number.
- Find the prime number using the C program.
- Find all prime numbers up to n using trial division and Sieve of Eratosthenes algorithm.
- Check date validity in C?
- How to use if in C programming.
- C language character set.
- How to use C if-else condition?
- How to use for loop in C?
- Elements of C Language.
- Data type in C language.
- Operators with Precedence and Associativity.
- 100 C interview Questions.
- 5 ways to find factorial of a number in C.
- C Program to find the Range of Fundamental Data Types.
- Fibonacci Series Program In C: A simple introduction.
- How to use atoi() and how to make own atoi()?
- Program to check leap year in C language.
- How to use the structure of function pointer in c language?
- Create a students management system in C.
- Create an employee management system in C.
- Top 11 Structure Padding Interview Questions in C
- File handling in C.

4 comments